ON THIS PAGE, YOU WILL FIND INFORMATION ABOUT THE WAYS YOU CAN GET SUPPORT ON ISSUES RELATED TO DOING YOUR RESEARCH. THIS VARIES FROM SUPPORT IN GETTING FUNDING, ETHICAL REVIEW, DATA MANAGEMENT, AND MORE.
Jump to:
ABOUT US
FUNDING AND GRANTS
Mandatory Knowledge Safety Check
Do you have plans to establish an international collaboration or to work with partner organisations in an international consortium?
Then it is compulsory to fill out one of the "Checklist Knowledge Security" well in advance of submission of the proposal. This also applies when you are submitting a grant within a consortium, e.g. for a Horizon-call, for an EDF call, for an NWO call, in which non-EU partners participate. Information provided by you via the "Knowledge Security Checklists" enable the Team to carry out an initial risk assessment. It only takes 5 minutes to start the procedure. The earlier you fill out the checklist, the better it is. The Knowledge Safety Team (KST) is ready to assist you throughout the entire process.
Please note that restrictions on collaborations and partnerships apply to certain countries. For more information, visit the page "Restrictions - Search by country".
(personal) GRANT SUPPORT
GRANTS SUPPORT
The grant & project advisor for BMS faculty is Sofia Mutlu-Numansen. She can support in linking your research ideas to grant opportunities, building a consortium, and editing your proposal drafts. She is your first contact person for anything research grant related. It is important to contact her from the moment you think of applying for a grant. This way she can have an overview of who is applying for what within BMS, and can link people to each other and support more pro-actively. Sofia works closely together with the Grants Office at central level (SBD-office) and other grant support officers all over the university.
Note: for questions regarding educational grants (e.g., Comenius), go to the BMS Teaching Academy. For questions specifically regarding Erasmus+, go to Janke Rademakers (Coordinator Internationalisation in Research).
An overview of recent calls is available on the SBD news page. In addition, an overview of health related calls can be found on the TechMed intranet. SBD has organized and recorded many infosessions, these recordings can be found here. Furthermore, you can search for funding opportunities in a new system for finding funding: Research Connect yourself.
PERSONAL GRANTS SUPPORT BMS
Personal grants are bottom-up and researcher-driven grants that enable researchers to strengthen their scientific career and conduct projects in their own line of research. Through such projects, researchers can explore new opportunities and directions within their field, which in turn can lead to new ambitious research projects.
Personal grants are often seen as prestigious seals to individual research careers, especially for early- or mid-career researchers. And, while several developments within the scientific community point to an increasing focus on Team Science, one can easily argue that enabling (young) talent to apply for personal grants can be considered a team effort as well. In fact, being successful in the highly competitive arena of personal grant programs, requires a lot of time, effort, and help from others. Therefore, the BMS faculty finds it important to additionally invest in supporting researchers with the acquisition of personal grants, next to the already existing support from the SBD-Grants Office.
Timeline for Personal Grants
Below you will find a short overview of personal grants aimed at different stages in researchers’ careers. Importantly, extension clauses apply to all grants for parents, and to most on grounds of training, care responsibilities, or sick leave, supporting efforts to increase diversity and inclusiveness through these programs. You can check your eligibilty for NWO and ERC yourself.
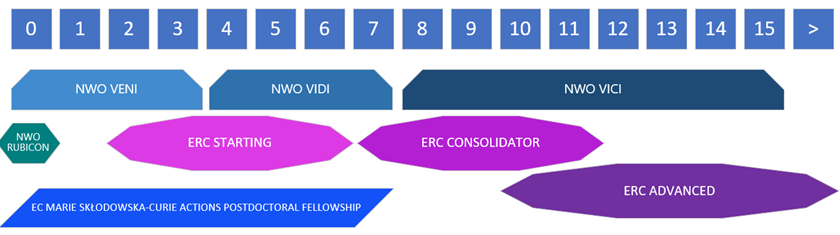
EMBEDDING GUARANTEE VENI & VIDI
NWO will ask candidates for an 'embedding guarantee' in their application for Veni and Vidi funding. In other words, researchers can only submit applications for Veni and Vidi funding with the support of their Department & Section Chair and the BMS Faculty Board.
EMBEDDING GUARANTEE VENi and vidi
Requests for a Veni embedding guarantee need to be submitted by the Department chair to the Faculty board before 31 May for VIDI the deadline is 8 September. The BMS procedure for requesting a VENI and VIDI embedding guarantee by the Faculty Board:
1. Section chair and candidate: agree with the candidate’s project proposal, and taking into account the consequences of grant acquirement for the section (i.e. in terms of the employment contract and time/topic dedication), and how the proposal is aligned with the BMS Research focus. Subsequently, the Section chair aligns with the Department chair on candidate(s).
2. Department chair sends (BEFORE 31 May (VENI) or 8 September (VIDI)) an email (entitled 'Embedding guarantee [name candidate]' to 'BMS dean', cc to: Section chair, candidate, and, Sofia Mutlu-Numansen.
The email explicitly states:
- section & department chair's consent with the candidate's project proposal,
- a statement that they both take into account the consequences of grant acquirement for the department/section (i.e. in terms of employment contract and time/topic dedication. Please discuss employment consequences explicitly with the HR advisor of your section to avoid unpleasant surprises);
- a statement that the candidate will be allowed time to write the full proposal.
- a quarter A4 motivation how the VENI/VIDI proposal is aligned with the BMS Research focus (we need this input to draft the guarantee);
- please attach CV of the candidate and a short (about 300 words) summary of the proposal. Instead, a concept of the pre-proposal is also sufficient.
3. After the Faculty Board meeting end June (VENI) or September (VIDI), a confirmation email will be sent including the positive/negative advice to chairs and candidate, and i.a. the embedding guarantee.
4. Around the NWO submission pre-proposal date we ask the candidates to reply (to all) to the received confirmation email and attach his/her completed pre-proposal. This is to check correspondence with the earlier received documents on which the embedding guarantee was based, and for our archive.
ELIGIBILITY CRITERIA FOR PERSONAL GRANTS
Instrument | Eligibility | Restrictions | Scheme | Deadlines |
Rubicon | Apply within 1 year after obtaining PhD | All nationalities Employed at NL institution for at least 3 of 5 years preceding application Max 1 application to Rubicon | 1-2 years Post-doc abroad ~65kEU/yr | Three deadlines per year. |
VENI | Apply within 3 years after obtaining a PhD Extensions may apply* | All nationalities Research must be conducted in NL Max 2 applications to VENI | 3 years of research in NL 250kEU | January |
VIDI | Apply within 8 years after obtaining a PhD Extensions may apply* | All nationalities Research must be conducted in NL Max 2 applications to VIDI | 5 years of research in NL + research staff 800kEU | October |
VICI | Apply within 15 years after obtaining a PhD Extensions may apply* | All nationalities Research must be conducted in NL Max 3 applications to VICI | 5 years of research in NL 1.5MEU | March (Pre-proposal) End of August (Full proposal) |
ERC Starting Grant | 2-10 years after obtaining a PhD, measured on 1 January Extensions may apply | Resubmission restrictions apply At least 50% time involvement of PI | 5 years project, 1.5MEU | October |
ERC Consolidator Grant | 8-15 years after obtaining a PhD, measured on 1 January Extensions may apply | Resubmission restrictions apply At least 40% time involvement of PI | 5 years project, 2.0MEU | February |
ERC Advanced Grant | senior/ established PIs | Resubmission restrictions apply At least 30% time involvement of PI | 5 years project, 2.5MEU | August |
MSCA IF European Fellowship | PhD Degree or 4 years of research experience after MSc | Mobility to NL from any other country (less than 12 of past 36 months in NL)
| 1-2 years project 83kEU/yr | September |
MSCA IF Global Fellowship | PhD Degree or 4 years of research experience after MSc | Mobility to non-EU country (less than 12 of the past 36 months in that country) Mandatory return phase | 1-2 years abroad, 1 year in NL 83kEU/yr | September |
* NOTE: possibility for extension to the time limit for Veni, Vidi, Vici applications on the grounds of care responsibilities, pregnancy, illness, and/or training in a clinical specialism. See FAQ NWO. Biological mothers who have given birth to one or more children are granted a standard extension of eighteen months per child. Other parents (fathers and non-biological mothers) are granted a standard extension of six months per child that is part of the applicant’s household
BUDGETING PROJECT APPLICATIONS (CALCULATION)
For support on costing and pricing in the application phase of your project contact Martin van Ooijen or Renate Masselink-Veldschoten (based on the department you work in). For more information see BMS financial affairs intranet and check who you need to get in contact with.
ENGAGING IN A COOPERATION WITH FOREIGN PARTNERS? CHECK EU SANCTION LIST!
We make you aware of the existence of the ‘EU sanction list’
Pay attention to this list and restrictions, before engaging in a cooperation agreement, contract or license agreement. The UT may not be allowed to collaborate with people/institutions in countries as mentioned on this list, depending on the specific restrictions. Ask our legal advisors for advice.
It is particularly of interest on relations with people/partners in countries that are on the sanction list and responsibilities for those who want to work with partners on what is classified as ‘Dual-Use research’ (goods, software, and technology that can be used for both civilian and military applications). Dual-use research can also refer to knowledge transfer, workshops, training and training materials, software, materials, sensors, and other equipment. For cooperation with international partners on dual-use research, and export a permit is required. European guidelines for research misuse.
In case of doubts or questions, please contact the BMS coordinator internationalization; Inge van Haare
HR EXCELLENCE IN RESEARCH
 The European Commission recognizes with the 'HR Excellence in Research Award' the institutions which make progress in aligning their human resources policies to the 40 principles of the Charter & Code, based on a customized action plan/HR strategy. The implementation of the Charter & Code principles by research institutions render them more attractive to researchers looking for a new employer or for a host for their research project.
The European Commission recognizes with the 'HR Excellence in Research Award' the institutions which make progress in aligning their human resources policies to the 40 principles of the Charter & Code, based on a customized action plan/HR strategy. The implementation of the Charter & Code principles by research institutions render them more attractive to researchers looking for a new employer or for a host for their research project.
The UT is allowed to use the 'HR excellence in research' logo. We encourage you to indicate this when acquiring for (European)funding.
THE BMS LAB
THE BMS LAB can support in project acquisition (technology, data), Hardware/software tools, Lab facilities, Data Management, Computing and Storage, Development, Surveys
Get in contact with the Managing Director: Dr. ir. Jan Willem van t'Klooster or with THE BMS LAB
Strategic Research Fund
BMS STRATEGIC RESEARCH FUND
The BMS Faculty Board has reserved an amount of €300k for the BMS Research Themes jointly to support researchers’ collaborative grant acquisition activities, especially where these involve research consortia. The Strategic Research Fund aims to support applications for collaborative grants and other strategic acquisition activities (e.g., contributions to the content of new calls, agenda setting in Brussels).
WHO CAN APPLY?
The fund is open to all BMS researchers, juniors and seniors.
WHAT CAN BE FUNDED, TO WHAT VALUE?
The funding aims to provide support mainly for the following activities:
- Preparation of a grant application targeted at a specific call, which is in line with the BMS Research Strategy.
- Consortium-building activities in readiness for anticipated calls.
In particular, the fund supports the following activities:
- Professional external project management/proposal writing services on a consultancy basis
- Event costs for hosting meetings with collaborators.
- Workshop costs, e.g., to engage regional partners.
- Graphic design and language editing
- Individual proofreading of grant applications (only when not covered by the Grants Office).
- Travel costs related to Horizon Europe brokerage events
This list is not exhaustive, applications may also request support for other activities related to grant acquisition. Please note that the purpose of the call is to support grant acquisition, not the financing of research as such.
The Theme Chairs coordinate the Fund. We have implemented a flexible and ‘rapid-response’ process to ensure that applicants can ask for various types of support while receiving a fast answer so they can respond rapidly to funding opportunities. In addition, we strive for fairness in distribution of the Fund across research themes, departments, and researchers.
For applications of more than €20.000, or deemed ‘high-risk’ by the Theme Chairs, the Faculty Board will decide based on advice from the Theme Chairs.
The SRF cannot be used for hiring student assistants or for travel costs. We have noticed some misunderstandings in this regard, so we want to clarify that these expenses are not eligible for funding.
While the SRF generally does not fund travel costs, an exception has been made for travel expenses related to Horizon Europe brokerage events. We believe that attending these events significantly enhances opportunities to form consortia for major Horizon grants.
2. Initial Screening: Sofia Mutlu-Numansen (BMS Strategic Grants Advisor) conducts the first review to ensure the application aligns with the BMS Grant Strategy and includes all required information.
3. Evaluation by Theme Chairs: Complete applications are evaluated by the Theme Chairs during their monthly meeting.
4. Outcome: Following the evaluation, applicants will receive feedback on their application with one of the following outcomes:
- Approved: The application is accepted for funding.
- Rejected: The application is declined, with a clear explanation provided.
- Revise and Submit: Additional information is needed, and the applicant is asked to provide further details.
BMS Open Access Fund
BMS stimulates Open Science, as from 2019 the Faculty Board of BMS made OA funds available. The BMS Open Access fund 2026 is available. Noting, however, that funds could be depleted before the end of the year. As APCs still increase, and because of (unforeseen) BTW costs on top of the invoice, we decided to raise the reimbursement.
BMS will reimburse (partly) publication costs for (high-quality) open-access journal articles or books/book chapters accepted in the period January-December 2026. Reimbursement depends on the criteria (see above link) and needs to be requested and paid by the section first before the end of 2026.

BMS PhD Fund
#CALL IS CLOSED --> FUNDS DEPLETED FOR 2025
Sometimes, opportunities arise in your PhD project that may benefit your professional development, but which are not accounted for beforehand. Often, sections cannot financially support these (unexpected) opportunity-driven activities out of the planned PhD-project budget. In case the activities not only result in the scientific-career growth of you as a PhD but also positively contribute to the knowledge/expertise of our faculty BMS, you can apply for (partial) funding from the BMS PhD Fund. We have around 3 submission dates during the year.
DATA MANAGEMENT, STORAGE, AND PRIVACY
RESEARCH DATA MANAGEMENT (RDM) (e.g. storage, DMP, FAIR)
Each individual researcher or research leader is responsible to draw up a data management plan. He or she should do this at the start of the research project, hence a DMP is a living document and will be updated during the project. During the research, you should actively follow up on the agreements made in this plan.
DMP-templates
There are many templates available for writing a DMP. To write your own DMP, please use the University of Twente’s DMP Template UT. Note that NWO, ZonMw, EU approved the UT dmp-template, so you can upload our own completed template by these funders.
Are you writing a data management plan (DMP) as required by your funder, or does the funder have questions regarding management of your research data?
Make sure you check the UT support on Data Management (and the course for PhD students), BMS Datalab Research DataManagement, UT and BMS data policies and Guidelines on personal information.
We have a multidisciplinary team with different specialties that can assist you in finalizing your DMP and support you on various aspects of research data management: datastewards-bms@utwente.nl (Datastewards BMS are Minsi, Deniece); all aspects of research data management: e.g. writing a data management section/plan for projects, data storage/sharing/archiving, repositories & data management course), Lyan Kamphuis-Blikman (privacy, personal data, informed consent procedures), THE BMS LAB (storage and data management details).
Get in contact with one of our BMS Datastewards (Minsi, Deniece) via the shared mailbox: datastewards-bms@utwente.nl
Working days: Monday, Wednesday, Thursday
RESEARCH DATA STORAGE / SHARING / ARCHIVING
BMS faculty covers the UniShare costs for BMS staff. Unishare facilitates secure data sharing and synchronization among partners from multiple institutions. UniShare allows team members to store, update, and share data securely, with all research data stored and backed up safely (ISO27001/NEN7510) in the datacenters of the University of Twente (UT). Access control can be managed by the project leader or Principal Investigator (PI). The steps on how to apply are on the intranet.
More information on BMS Datalab Data storage and Sharing/Archiving. Also for students!
Also, check the micro-lectures designed for students on how to handle your research data.
For more details, including a help functionality for choosing the best storing and sharing solution for your research data, see the Research Data Management page (by LISA)
UT offers a Virtual Research Environment (VRE) for its employees (check video!!). If you are a UT researcher looking for flexible, efficient, and scalable computing infrastructure to perform simulations/calculations, the Virtual Research Environment (VRE) could be a good option for you.
UT supports archiving research data at the end of a PhD or research project. Areda, the institutional data archive, ensures secure, certified storage for long-term preservation in line with the UT RDM policy. Areda enables individual researchers and research groups to sustainably store their research data for the long-term. Areda supports all types of static data and allows adding metadata and documentation via the UT research information system, Pure.
Datasets (zip or tar) are uploaded to your research group’s “bucket,” accessible to all group members. Access can only be restricted through encryption, which is required for personal or confidential data. Digital informed consent forms and pseudonymization keys must not be stored in Areda; These must be stored encrypted and separately from the anonymized (or pseudonymized) data. Store them encrypted in JOIN or on the p-drive instead. Although folders can be created, it is recommended to store project data as a single archive of zip-files with a structured dataset.
For instructions, please see the Archiving datasets in Areda: a guide. For assistance, contact the BMS data stewards or visit the Areda service portal.
PRESERVING AND PUBLISHING DATA (FAIR)
Research data is often regarded as the crown jewels of science. It forms the basis of the results of scientific work. Data preservation or archiving aims in the first place at preventing physical data loss or destruction and securing the authenticity of data. Besides, it contributes to the quality and impact of your scientific work by enabling verification and possible reuse, for instance for further analysis or follow-up, new research, or as a contribution to a data resource for the scientific community. Preservation of data is also needed in case of a data publication: a journal article about a specific data set.
Read more on preserving and publishing data FAIR, and the long-term archiving of research data at UT via Areda.
DATA REUSE
The aim of open science is that researchers reuse other parties' research data and services where possible and make their own data available as far as possible.
Think about reuse of existing datasets in your research. Check UT Research support for more data sources.
FUNDER REQUIREMENTS
Research funders NWO, ZonMw, and the EU have a data management policy that affects grant submission. They all ask you to write a data management plan within a certain amount of months after the start of your project. NWO and the EU also want you to answer specific questions as part of the submission process (data management section) about the way you are going to manage the research data.
For NWO, calls for proposals will include a data management section in which the researcher should answer a number of short questions. LISA has developed guidance with examples for answering these questions.
PRIVACY (GDPR)/ USE OF PERSONAL DATA IN RESEARCH
CAREFUL USE OF PERSONAL DATA IN RESEARCH UNDER THE GDPR
When conducting scientific research, personal data may be processed. This could be, for example, data of persons who complete surveys or participate in a study, but also data from social media or tracking data. The DPO & PCPs of the UT made a document that contains a Decision aid & Flow chart with further explanation is now available to help researchers comply with the GDPR
When you collect or use personally identifiable data of persons (e.g., respondents, informants, test subjects, interviewees) who participate in your research, you have to comply with the GDPR privacy law. If possible, process the data of the persons in your research anonymously right from the start or as soon as possible, anonymous data does not fall under the GDPR law. You can also work with pseudonymization (make use of coding), in that case, make sure you keep the key secure, as this data falls under GDPR regulations. More information on this can be found on the UT privacy website and on BMS Datalab.
Also, make sure that you know the rights of your participants and use an informed consent procedure when processing their personal data.
Codes of conduct, guidelines, and legislation
For an overview of relevant guidances check UT Policy and legislation page, covering privacy and codes of conduct specially drawn up for researchers, i.e. the VSNU code of conduct on the use of personal data in research, and the Code of Conduct for Health Research for dealing responsibly with (personal) data and human tissue in Dutch health research.
Processor agreement
When you work with an external party (processor) that helps you processing research data, you may need a processor agreement in case the research data is identifiable to individual persons (also the case if data is coded/pseudonymized). Get in contact with the PCP of BMS: Lyan Kamphuis-Blikman to sort out if this is necessary.
Register your research with personal data (Report data processing)
The UT has a documentation obligation for data registrations of personal information. This means all research that processes data of persons. Therefore, employees and students (see FAQ) need to register their research.
Read more info and the link to the UT GDPR Registration tool for processing Personal Data
Contact
For the BMS faculty, Lyan Kamphuis-Blikman is the Privacy Contact Person (PCP). The UT Data Protection Officer (DPO) can also be contacted.
UT DIGITAL COMPETENCE CENTRE (DCC)
The UT Digital Competence Center (DCC) is the hub for expertise on Open Science - Especially Fair Data and Open Access -, Digitalization of Science and Research ICT Facilities.
Every month the DCC picks a topic to put in the spotlights:
- Check previous Thematic sessions
- Read Interviews on how DCC experts have helped other (BMS) researchers to make their research data FAIR and/ or open, or with questions about Open Science, Open Access or ICT for Research.
- Do not miss announcements of the DCC: subscribe to the newsletter
BMS DATALAB website
BMS Datalab webpage sets out how to handle research data safely, legally, ethically correct, and methodically soundly.
(OPEN ACCESS) PUBLICATION, preregistration, and your Research Output (RIS-PURE)
PUBLICATIONS AND MORE LIBRARY RELATED SUPPORT
The BMS Information specialists (Marit or Kasandra), infospecs-bms@utwente.nl) can support you on topics like Choosing a suitable journal for your scientific work (Publishing), Open Access publication/Open Data (see more below under Open Science heading), Copyright & Referencing, Literature searches, Searching, finding and processing scientific information, Bibliometrics and visibility, and more (add ref).
OPEN SCIENCE: publishing Open Access and Open Data
Open Science is the practice of science in such a way that others can collaborate and contribute, where research data, lab notes and other research processes are freely available, under terms that enable reuse, redistribution and reproduction of the research and its underlying data and methods. Thus, Open Science is about more than only publishing Open Access, but on this page we limit it to support for OA publication and data.
 UT Open Access info page
UT Open Access info page
Find out what the advantages of open-access publishing are, how to select a high-quality journal in your field for open-access publishing, how to publish open access for free as a UT author, and how to easily open up your closed publications. UT policy on Open Access Policy summary
UT policy on Open Access Policy summary
For the full text on UT policy on Open Access, check the UT OA website. Does the journal of your choice allow open access? --> check the Journal Browser.
Does the journal of your choice allow open access? --> check the Journal Browser. Flowchart Publishing articles open access as a UT author
Flowchart Publishing articles open access as a UT author
Follow the steps in this flowchart. It will lead to an open version of your article, no matter what journal you publish in. BMS OA fund 2025
BMS OA fund 2025- Get in contact with BMS information specialists
infospecs-bms@utwente.nl  Open Science Guide by consortium UKB, UNL, DANS, NWO
Open Science Guide by consortium UKB, UNL, DANS, NWO
This guide is aimed at PhD candidates, Research Master Students, and early-career researchers from all disciplines, designed to accompany researchers in every step of their research.
GOAL 100% OPEN!
Our aim is to make 100% of our research publication output Open in some form. How can we all contribute to this goal?
- Always consider publishing in (high-quality) open access journals, listed in the Directory of Open Access Journals (DOAJ). Some funders (e.g. NWO) let you budget for OA costs before your project starts.
- In many ‘hybrid’ OA journals, national deals let you publish OA for free. Check via the UT Journal Browser and request OA upon acceptance. Be sure to request OA under this deal upon acceptance of your article.
- Publisher Emerald offers a limited number of OA vouchers shared by Dutch universities. UT researchers can use them to publish for free in subscribed Emerald journals or on Emerald Open Research. After your paper is accepted, the editor will contact you (see their illustrated workflow). Vouchers run out early each year—if none are left, contact the BMS information specialist about a possible refund via the BMS OA fund.
- OA after six months: Automatically open in UT Research Information. Check UT Open Access for info.
- If your research was funded by NWO or ZonMw, you can publish your results Open Access for free via Europe PMC , meeting your funder’s immediate OA requirement.
- Openjournals.nl is a free, open-access platform for Dutch academic journals, launched in 2021, using a diamond model with no costs for authors.
Choose the right journal for your research
The website 'Think. Check. Submit.' helps researchers identify trusted journals for their research.
Through a range of tools and practical resources, this international, cross-sector initiative aims to educate researchers, promote integrity, and build trust in credible research and publications.
Predatory Publishers
Be aware of predatory publishers! With the start of open-access publishing also the predatory publishers came into existence. These predatory publishers are dishonest and lack transparency and exploit the author-pays model with high fees. They aim to dupe researchers, especially those inexperienced in scholarly communication. They set up websites that closely resemble those of legitimate online publishers, and publish journals of questionable and downright low quality. Read more.
Article (Dutch) on how you recognize Predatory publishers
Get in contact with the information specialist of BMS if you doubt about a journal.
Research Information System (Pure)
Following the UT Open Access Policy to research results you:
- must upload the Final published version of your publication (Publishers PDF) in the UT Research Information System (Pure) AND
- you are strongly encouraged to also upload the Accepted Author version of your non-OA publications. That is the final full-text version (after changes based on peer review and editorial comments) but without the layout of the publisher.
The UT library always validates the open availability of your publication.
Read more about RIS-Pure functionalities and opportunities to register publications, activities, prizes, awards, projects, datasets in a separate support topic.
FUNDS OPEN SCIENCE
BMS Open Acces Fund
Read more on the BMS OA fund 2025, check requirements and how to request.
In the last years (starting from 2019) we offer BMS researchers financial support in OA publishing. The UT Open Science Fund ceases to exist as of 2019.
For NWO funded projects: Books Open Access
Planning to publish an academic book Open Acces and is the publication resulting from an NWO funded project? Then you can apply as from 1 June 2020 onwards continuous for the Open Access Books call by NWO. News message UT.
NWO Open Science Fund
NWO opened a new funding instrument in 2021: the Open Science Fund. It aims to support researchers to develop, test, and implement innovative ways of making research open, accessible, transparent, and reusable (FAIR), covering the whole range of Open Science.
The Dutch Research Council NWO is making 500,000 euros per year available for this program, initially until 2023. A maximum of 50,000 euros is available per project.
At this moment (nov'21) there is no call available, it will be back in 2022. Check NWO info.
OPEN DATA
Funders (e.g. ZonMW, NWO) also expect you to archive your research data belonging to a publication or a dataset belonging to the whole project and make it Open or FAIR. Find out more about archiving your research output.
For questions related to Open Data, you can reach out to our Data Stewards.
Once you archived your research data make sure you put it in RIS-Pure as well, read more about this under our RIS-Pure support.
Reuse
The aim of open science is that researchers reuse other parties' research data and services where possible and make their own data available as far as possible.
Think about reuse of existing datasets in your research. Check also UT Research support for more data sources.
PREREGISTRATION OF YOUR RESEARCH
PREREGISTRATION & REGISTERED REPORTS
Preregistration is the practice of submitting a research plan to a (public and trusted) registry, specifying the study's hypotheses and (analytical) methods, before the start of data collection or the analysis of a dataset. Registered reports are similar to preregistrations because they are also written plans including a study design and analytical plans. However, a registered report goes beyond that as it strives to become a published scientific article by itself, therefore including a peer-review step and decision to publish before data collection can begin.
Why should I preregister a study?
Preregistration commits researchers to the hypotheses and analytical approach of their study. In that way, it helps them avoid questionable practices and biases in research. For example, p-hacking or HARKing (Hypothesising After Results are Known). Above all, preregistration makes science more open, transparent, and potentially more effective.
The faculty of BMS is actively working (see interview above) to encourage and facilitate preregistration. By pre-registering, you become an example of open and good research for the faculty, the UT, and your peers and collaborators worldwide. Preregistration shows that you strive for quality in your research rather than quantity.
How can I preregister a study?
Two steps, (1) start by identifying a suitable registry for your study and then just (2) follow their submission guidelines. The faculty of BMS recommends the following options:
- Open Science Framework (free platform for open and collaborative research)
- AsPredicted (easy way to generate your own preregistration report)
- PROSPERO (prospective register of systematic reviews)
- ClinicalTrials.gov (database of clinical studies conducted around the world)
As seen above, some databases or registries focus on the preregistration of specific study designs. Importantly, keep in mind that preregistration does not necessarily need to be immediately public. The preregistration in a platform receives a timestamp and often a DOI (a permanent and citable link). Still, the preregistration can be embargoed and, for instance, made public around the same time than the results of a study. In any case, you should preregister before conducting any data collection (whether it is the first or an extra round), or before you begin with the analysis of an existing dataset.
What is the added value of Registered Reports?
While preregistration is often taking place on independent platforms, a ‘Registered Report’ is embedded in the typical processes of scientific journals. The methodological report is submitted to a journal and goes through the typical peer-review process. You are therefore adding another quality check to your research work, thus visualizing and recognizing the value of a study’s methodological design rather than just its (potential) results. The figure below visualizes this process.

Credits: This image is © Center for Open Science, used under a Creative Commons Attribution-No Derivatives 4.0 International License.
Once a registered report is accepted by the journal, data collection can start, with the added benefit that the methodological plan has been peer-reviewed. This also makes it possible that, in principle, the results of that study are already known to be of interest for the journal, whether they align or not with the study’s hypotheses.
The table below shows the differences between preregistration and registered reports.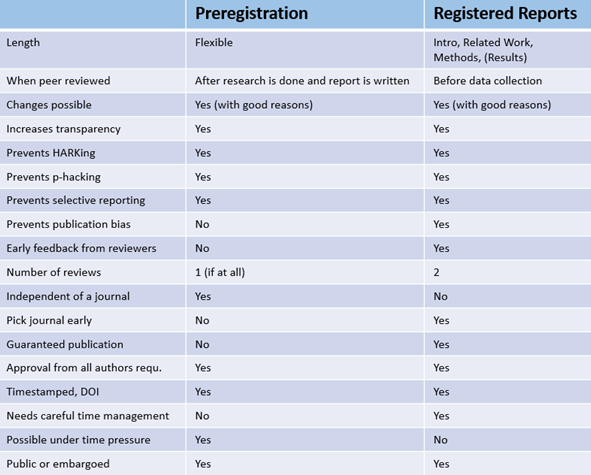
Credits: Markus Konkol, ‘Blog#3 – Open Science Kitchen on Preregistration and Registered Reports’.
Questions and support
For any questions or support with preregistration or registered reports within BMS please contact the information specialists (infospecs-bms@utwente.nl). If needed, the information specialist will put you in contact with other members of the support team (e.g. data stewards, research support coordinator).
Self-learning
Do you want to learn about preregistration and registered reports by yourself? We highly recommend you to read this page from the Center for Open Science and this blog from the OSCTwente. Below you can also find a reading list compiled by members of the ReproducibiliTea initiative.
UT RESEARCH INFORMATION SYSTEM (RIS-PURE)
PURE RESEARCH INFORMATION is the back-end system where researchers can showcase their research output, profiles, and activities to increase visibility, access, and impact. This information is published on a public portal.
For more information on the Research Information System (RIS) Pure see the UT RIS website (moved to UT service portal), especially the Quick Reference Cards (QRCs), or use the Manual and FAQ within the RIS Pure.
We also collected some do's and dont's when submitting research output to UT RIS-PURE.
NEW UT-Researchers: By default your profile is set to non-visible, please follow these instructions to activate.
We also have a help text available on how to add research output from previous/other employments.
If the direct links to the guides linked to on this page do not work anymore, look for the title on the infopage with quick reference cards.
SOME BASICS OF PURE:
PUBLICATIONS
![]() You can add these via your personal profile page in the Pure‐backend by a click on the arrow, next to the tab personal, this will bring up your options or use the big blue button ‘add new’. Several ways to add your output:
You can add these via your personal profile page in the Pure‐backend by a click on the arrow, next to the tab personal, this will bring up your options or use the big blue button ‘add new’. Several ways to add your output:
- Create research output from a template manually or from an online source (minimal effort).
- Enable the automated search profile to automatically import your publications (last 2 years) regularly into Pure. You will be notified by email if new ‘candidates’ are available to be imported.
- Register for ORCID (a unique identifier for a researcher) and read how to import your OCRID into Pure, import publications using your ORCID, and how to export research contributions from Pure to ORCID. A quick guide on ORCID with print screens is available as well.
- Via ris@utwente.nl you can indicate the publications that need to be added.
- Embed publications for a group or individual researcher: create your publication list on a website.
IMPORTANT: As UT has an open access (OA) policy please always upload the final published version and – in case of a non-OA article – the accepted author version to maximize the visibility of your work.
ACTIVITIES, PRIZES, PRESS/MEDIA, AWARDS
 Besides publications, you generate impact with your research-related activities, for your own and the faculty/UT its visibility these are valuable to add! Examples of relevant categories of Activities may be Editorial work, Membership of an external organization, Membership of Committee, Organization of an event, Consultancy work, Invited keynote talks, your Prizes, and Awards. Please also add relevant external positions, log in the backend of Pure, go to ‘edit profile’ scroll down until you see ‘Positions outside of the institution’ and add your external position, it will be shown on your Pure Portal.
Besides publications, you generate impact with your research-related activities, for your own and the faculty/UT its visibility these are valuable to add! Examples of relevant categories of Activities may be Editorial work, Membership of an external organization, Membership of Committee, Organization of an event, Consultancy work, Invited keynote talks, your Prizes, and Awards. Please also add relevant external positions, log in the backend of Pure, go to ‘edit profile’ scroll down until you see ‘Positions outside of the institution’ and add your external position, it will be shown on your Pure Portal.
NEW! REGISTER YOUR RESEARCH DATASET
![]() As of now, you can also register the research data* that belong to your publications, or a complete dataset of data collected in your project, produced and/or used for your research at the UT. When you describe your data and their location, others can easily understand and find them in UT Research Information and as such, in search engines such as Google Scholar. This is important when others want to verify and possibly reuse your scientific work (when they do, they always have to cite it).
As of now, you can also register the research data* that belong to your publications, or a complete dataset of data collected in your project, produced and/or used for your research at the UT. When you describe your data and their location, others can easily understand and find them in UT Research Information and as such, in search engines such as Google Scholar. This is important when others want to verify and possibly reuse your scientific work (when they do, they always have to cite it).
NOTE: Once you registered your dataset that belongs to a publication in RIS-Pure, make sure you also link your dataset to your publication in RIS-Pure: by adding your publication (research outputs) under the heading 'relations to other content' in the dataset registration form in RIS-PURE (explained in the guide above). The other way around is also possible, go to the registration of your publication in RIS-Pure, and add under the heading 'Relations' the registered dataset that belongs to the publication.
Have a look at how a dataset from your BMS colleagues is presented in UT Research Information.
*You cannot upload your research data to UT Research Information, but you can add a good description, metadata, and possibly a link (doi) to the location of the datasets, so others can easily find them. You can also show this information along with other content in UT Research Information, such as publications that are based on your data. This increases the visibility, access, and impact of both your research data and your publications. If you want to upload your research data to a trusted repository, then please do so in, for instance, 4TU.ResearchData or DANS. Once your data are available there, you can add the link to be presented in UT Research Information along with the description of your data. It will soon be possible to automatically transfer metadata from these repositories to UT Research Information.
HIGHLIGHT SPECIFIC RESEARCH CONTENT (PUBLICATIONS/ACTIVITIES) ON YOUR RIS-PURE PORTAL PAGE:
Pure has the functionality to highlight a selection of publications/activities on your personal RIS-Pure portal page. Login to your Pure account and go to 'edit profile' and then on the left to 'Portal profile'. Under the header 'Highlighted content' you can search in several content types the content you want to highlight.
PROJECTS
![]() Projects can't be added manually into Pure, they are loaded from Oracle Projects. Projects are not visible on the portal page yet, their visibility is set on restricted only visible in the backend of Pure. However, since recently (end'2020) we have the possibility to enrich the project with info (such as: good title, description of the project, participants and collaborative partners, a website link, related research outputs, applications/awards for this project) and prepare it for public visibility. As soon as the UT has a sufficient number of 'projects ready for public visibility', the UT can activate the visibility of 'Projects' in the Pure portal.
Projects can't be added manually into Pure, they are loaded from Oracle Projects. Projects are not visible on the portal page yet, their visibility is set on restricted only visible in the backend of Pure. However, since recently (end'2020) we have the possibility to enrich the project with info (such as: good title, description of the project, participants and collaborative partners, a website link, related research outputs, applications/awards for this project) and prepare it for public visibility. As soon as the UT has a sufficient number of 'projects ready for public visibility', the UT can activate the visibility of 'Projects' in the Pure portal.
Other possibilities to highlight the projects you are involved in are:
You can highlight your projects in a description on your Pure-profile. Go to ‘Personal Overview’ > edit profile > ‘Curriculum and research description’ > add profile information and choose type ‘projects’ and fill in the text box. The text under 'projects' cannot be shown automatically yet in People Pages (by ‘use text from Pure’), at the moment this is only possible for the text under 'research interest'. It will be possible soon.
Previous or planned upgrades of Pure.
UT research information website: https://www.utwente.nl/en/ris/
Faculty Managers BMS: Lyan Kamphuis-Blikman
Library RIS-team: ris@utwente.nl
PEOPLE PAGES and RIS-PURE connected
The information about your research output in RIS-PURE can be connected with your People Pages (check FAQ):
Description of your research
In your RIS-Pure profile go to 'edit profile' and then to the heading 'Curriculum and research description' and add information on several topics (personal profile, Research interests, Teaching, Projects). In your People pages, you can show the information that you update in RIS-Pure (from the field Research Interests) by selecting 'use text from pure' under the tab 'Research'.
Publications
Your publications registered in RIS-Pure are automatically shown on your People Page, but you may edit the number of presented publications or the period to display (in years).
Expertise
Based on words and phrases from your research output including a title and abstract, so-called 'Fingerprints' are constructed in RIS-Pure. These Fingerprints are exported to the field 'Expertise' in People Pages. More guidance on fingerprints can be found in a FAQ
It is possible to control fingerprints by 1) adding Abstracts to the metadata of your publications; 2) Removing fingerprints individually; 3) disable fingerprints in RIS-Pure.
In RIS-Pure you can also make your own 'Keywords' within your own RIS-Pure profile. Choose one of the (sub)categories listed from A-->Z and then you get textfields for free keywords which you can fill yourself.
Another option is to write a piece of text in your People pages profile under 'About me'. By doing that you can make a introducing text and end with a heading with expertises, and because the text will appear above the pre-set 'Expertises', these (wrong) expertises will be moved further down on the page and will not be immediately visible anymore. Instead visitors will first read your own introducing text including your own keywords.
ETHICS AND INTEGRITY
BMS ETHICS COMMITTEE (domain HSS)/ WEB APPLICATION
Ethical Review of Research at BMS
The Faculty of BMS requires ethical assessment for all research involving human participants and/or sensitive data about individuals, groups, or organizations. This ensures ethically responsible research practice.
Information about the procedure, principles, and criteria is available on the Ethics Committee BMS / HSS domain website.
For questions, contact: ethicscommittee-bms@utwente.nl
UT-wide Ethics Review
The University of Twente has a research ethics policy that assigns non-medical research to one of four domain-specific committees. While most BMS research is reviewed by the BMS/HSS committee, some projects may fall under other domains, such as CIS (cyber research) or NES (technology-related health research).
Submit your project via the UT Ethics Review Application.
Health-Related Research Support
The TechMed Centre supports university researchers with WMO applicability, medical-ethical review preparations, MDR compliance, and health technology implementation. Get in contact.
Knowledge Safety and Sanctioned collaborations
Knowledge safety: EU Sanctioned Universities and Institutes
International partnerships and collaboration are of high importance at the UT. Despite the opportunities and benefits, international collaboration also comes with certain risks - generally known as knowledge safety risks. Knowledge safety at the UT is defined as the protection of the UT community and infrastructure against:
a. the undesirable or illegitimate transfer of (sensitive) knowledge, materials, and technology to individuals, organizations, regimes or countries (including the transfer of controlled dual-use or military technology without compliance with current export control regimes).
b. covert influence by state and non-state actors. Such interference can include manifest itself through pressure to transfer knowledge outside the legitimate context of research /education projects, through pressure on students/staff to self-censor, to report, to change research topic, methods or results, through spreading of disinformation or through digital intrusions or cyber-attacks.
One example of illegitimate transfer of knowledge (under a) is the collaboration with sanctioned individuals, organizations, regimes or countries. More background information on the EU sanctions regime can be found here.
- One implication of the (EU and UN) sanctions regime for researchers is that no form of collaboration, whatsoever, is allowed with persons working for listed sanctioned universities & research institutes in Iran, Syria (also not by co-authoring publications and also not when it concerns ‘harmless’ topics). For North Korea, all scientific and technical cooperation is forbidden.
- Another implication for the UT community is that hiring or hosting people who have connections with sanctioned universities and institutes is also legally prohibited. For this we have developed a special process, that will be implemented through HR at BMS and central level. The list of sanctioned universities and research institutes in Iran and Syria can be found here.
It is important to note that research cooperation with or hiring staff from other universities is not prohibited. We want to be an inclusive university.
If you have questions feel free to contact the Knowledge Safety Office.
SCIENTIFIC INTEGRITY & SOCIAL SAFETY
HOUSE OF INTEGRITY
At University of Twente we have an integrated perspective and approach on integrity policies. We have an integrated integrity programme called ‘House of Integrity’ to structure and organize various integrity policies, regulations and practices. Our House of Integrity approach covers scientific, social and business integrity.
Scientific Integrity Programme
If you would like to familiarise yourself with current issues of scientific integrity, and current legal frameworks now governing integrity, you can apply for the Scientific Integrity Programme at UT. This programme is now available online and you can attend the subsequent workshop.
CODES OF CONDUCT UNIVERSITY OF TWENTE
The University of Twente has a number of codes of conduct related to integrity. Here you can find, e.g. the behavioral standard for everyone who is part of the UT community, the policy of the university in ancillary activities, which guidelines apply to professional scientific activities and various codes of conduct that apply, for example, to ICT and internet use or to (sexual) intimidation, aggression, violence and discrimination.
The codes are applicable to everyone who is part of the UT community: employees, students, and those representing the University of Twente.
CONFIDENTIAL ADVISORS
At the UT it is of utmost importance that everyone feels they have a safe and secure basis for their work and study that also makes it possible to conduct difficult or critical conversations when necessary. Students and staff must be able to address concerns, dilemmas and complaints within the UT, they need to feel they are safe to do so and feel assured their report or complaint will be taken seriously. Providing a safe university environment is recently underlined in a statement by all Dutch universities.
If you want to report undesirable behavior, you can get in contact with one of the confidential advisors for advice and support whenever you have to deal with unacceptable behavior, like intimidation, (sexual) harassment, aggression, violence, discrimination, bullying or stalking, or when faced with a conflict in your work situation connected to such behavior. PhD candidates, too, may call on the confidential advisor. Bachelor's and master's students may not, however. These students can approach any of the student counselors of their program should they be confronted with unacceptable behavior.
DUTCH AND EUROPEAN CODES OF CONDUCT SCIENTIFIC INTEGRITY
All those involved with education and research bear responsibility for upholding scientific integrity as specified in the Dutch and European codes of conduct for scientific integrity.
DILEMMA GAME SCIENTIFIC INTEGRITY
Looking for a way to address scientific integrity in your department? There is a dilemma game focusing on professionalism and integrity in research available, which is developed by Erasmus University Rotterdam (EUR). The dilemma game 'Professionalism and integrity in research' uses many common dilemmas in science and invites discussion on the subject.
Dilemma Game Scientific Integrity
SCIENTIFIC INTEGRITY COMMITTEE (CWI), ADVISORS, AND COMPLAINTS PROCEDURE
POINT OF CONTACT FOR THE COMPLAINANT
The first point of contact is the university's confidential adviser for scientific integrity (for the complainant), Prof.dr.ir. Olaf Fisscher. The complainant is advised to speak with this confidential adviser before filing a complaint to the committee. Possible violations of scientific integrity, as well as any follow-up steps, can be discussed with him in all confidence. Prof. Fisscher can be reached at o.a.m.fisscher@utwente.nl.
For the accused staff member of the UT who have faced a complaint with regards to their integrity can, if they so desire, be assisted by the independent university's confidential adviser for the defendant, Prof.dr Alfred Stein, who can be reached at: a.stein@utwente.nl. The confidential adviser knows the rules and procedures and can support the defendant. The defendant can share his or her doubts and concerns with this confidential adviser and this confidential advisor can also provide aftercare services.
COMPLAINTS PROCEDURE
The UT has a Scientific Integrity Complaints Procedure in order to protect and guarantee scientific integrity. This procedure provides a system for reporting and dealing with possible violations of scientific integrity. This procedure is consistent with the national LOWI regulations.
METHODOLOGY AND FACILITIES
USE TECHNOLOGY IN YOUR RESEARCH (BMS LAB)
THE BMS LAB provides support on: Hardware/software tools, Lab facilities, Advice in using tools/facilities, Advice in how to implement technologies into education, Support for project acquisition (technology, data), Data Management, Computing, Data processing and Storage, Development, Surveys, Knowledgebase on algorithms/equipment use/data processing (e.g. Audio transcription)/procedures.
SONA test subject pool & Recruitment participants
The test subject pool system SONA can be used if you need student participants for your research sample. You can recruit participants for your research via SONA. To include your study in this system, you first need to submit your research project to the BMS Ethics Committee via the web application. As part of the web application, you will be asked if you wish to make use of the Sona test-subject system (Sona Systems) to recruit participants to carry out your research. For more information on the procedure and rules for the recruitment of participants read the SONA website.
The Sona test-subject system is coordinated by the research secretary’s office (Shaunie Schutten, Ravelijn room 3244, tel. (053) 489 1291, email: test-subjects-bms@utwente.nl).
Recruitment of participants
As of June'2023 UT has a website 'Meedoen met Onderzoek' (Dutch) for people outside the UT to check if there are research projects searching for participants, and if people like to be informed on the research in order to decide if they want to participate. You as a researcher/student can contact Renske van Wijk via meedoen@utwente.nl to inform if your research project can be shared on that page to help you recruit participants.
METHODOLOGICAL/ANALYTICS SUPPORT
The department OMD can support researchers on Research methods and Data analysis.
Contact: Henk van de Kolk
For students, the Methodology shop is available for methodological questions, help with statistics, manuals and a database with micro-lectures.
BDSI - Behavioural Data Science Incubator
The aim of Behavioural Data Science Incubator (BDSI) is to spark innovation and collaboration in data science that involves human behaviour: to accelerate and inspire data-driven research within BMS that uses statistical models, machine learning, or simulation techniques.
BDSI will support researchers and promote good research practices in all steps of the research cycle:
- data gathering and governance,
- model building, training, and validation,
- visualization and reporting
BDSI will organise courses, workshops and networking events on these topics, and provide training in the R and Python programming languages on all skill levels. We support the writing of research grants. By building a strong community, we aim to connect researchers in BMS with each other, with other UT research groups, and the outside world.
BDSI is run by four representatives from all BMS clusters. If you have questions or ideas, or you want to get involved, contact your BDSI representative (meet the team):
- Karin Groothuis-Oudshoorn, c.g.m.oudshoorn@utwente.nl (TPS)
- Martin Schmettow, m.schmettow@utwente.nl (DDS)
- Abhishta Abhishta, s.abhishta@utwente.nl (HBE)
- Robert Marinescu-Muster, r.marinescu-muster@utwente.nl (HIB)
- Stéphanie van den Berg (chair), stephanie.vandenberg@utwente.nl

PhD Portal and policy
BMS PhD portal (intranet)
For more information for PhDs working at BMS and our BMS PhDs for PhDs initiative, see the BMS PhD Portal (Intranet).
And check the special News (and Events) page for BMS PhDs as well, for the announcement of discounts, grants, workshops and more.
External PhD Policy and Registration
In accordance with UNL guidelines and UT rules and regulations for PhD candidates, BMS specified a uniform process for registering and policy guidelines applying to external PhD candidates (i.e., PhD candidates not employed by the university), including fees and waivers. For requesting approval for a new external PhD candidate, a standard form can be used and sent to the Dean’s Office. In case the links do not work, make sure to be logged in on the intranet before trying again.
IMPACT
Impact Pathways, Impact Cases, and Indicators
Impact Pathway
Using an impact pathway is an effective way to plan for future impact and going beyond just what you are doing. An impact pathway tries to bridge what you do (activities) to what a future state where something has changed (impact). You can see this illustrated in the image below, where the steps can be described as:
- Inputs: What academics need (e.g., a grant).
- Activities: What academics do (e.g., literature review, interviews, lab work, surveys).
- Outputs: The products of research (knowledge and tangible “products”, like a publication or prototype)
- Outcomes: People are aware of and are using the outputs (e.g., a healthcare provider using your proposed way of working, or your theory becoming used in a field)
- Impact: effect on… (going beyond usage: what is actually changing? Is the “use” sustained? Who benefits?)
When using an impact pathway, you start at the desired impact and then work your way back. This also fits the Impact by Design approach of the BMS Position Paper on Impact, where impact is a continuous part of our work, not an afterthought. You may also recognise this approach from NWO or Erasmus+ calls for instance.
Sometimes multiple paths contribute to the same impact. Think of an overarching envisioned impact and multiple work packages that contribute to this. Or how your education and research with make an impact but sometimes in different ways. As such, you could also “stack” pathways that all lead to a same impact.
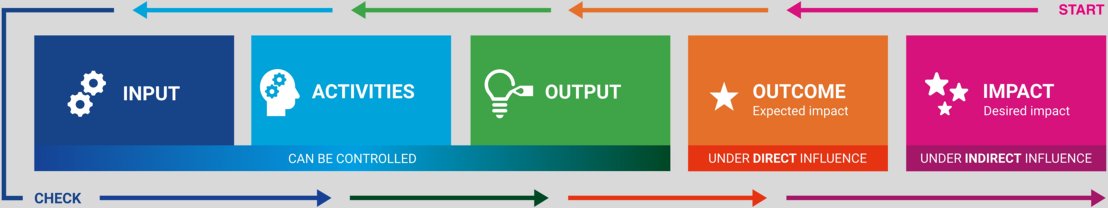
Figure: a model impact pathway, adapted from the Erasmus+ Impacttool
But you can't control everything! Sometimes researchers feel that they are solely responsible for their impact, but this is not the case. The further you are in the impact pathway, the less control you have. This is visualised below (you may recognise this from the NWO "Working with an Impact Plan" module). For example, you are in control of the contents of your publication, intervention, or prototype, but who is citing/using this, is something you can influence but not control. When talking about future impact, you can describe how you set up your work so that the chance of future impact is high.
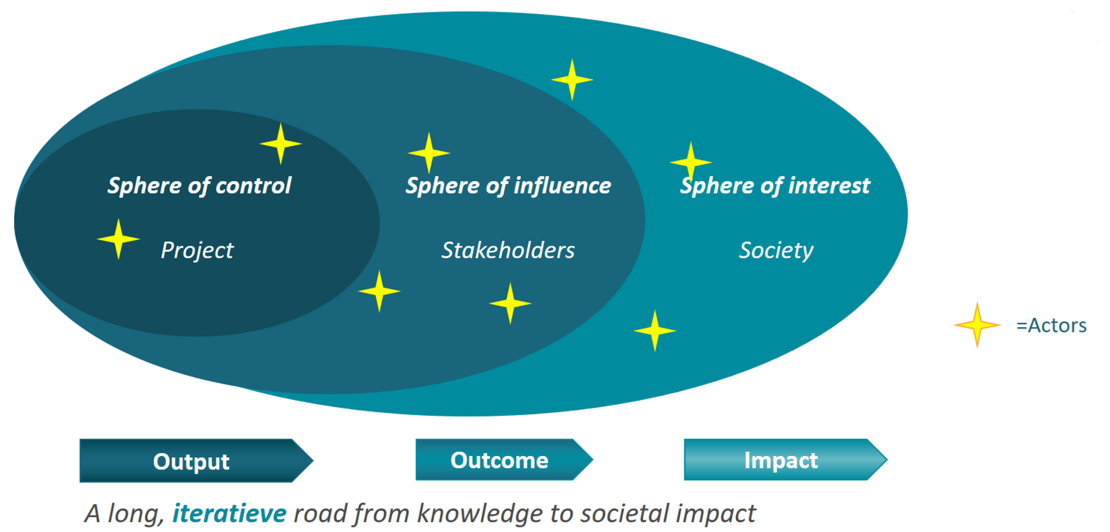
Figure: spheres of control, influence and interest
Impact Case
If you wish to make your past impact explicit, you can compose an impact case for a certain project or a research line. "Impact cases represent a portfolio of research around a central theme, line of research or topic. Impact cases are a comprehensive impact assessment tool to determine the contribution of a university, a group and/or individual researcher's make to society and the economy." (University of York) To guide you in developing your own impact case, a template has been developed, see below.
IMPACT INDICATOR framework
Making impact explicit can be quite challenging. Every project is different, so a generic set of e.g., 7 indicators does not exist. Instead, one can opt for context-sensitive indicators that match well with the goal of that specific project (per the Impacty by Design method). The Impact Indicator Framework provides a wide set of generic indicators that can help you find indicators that fit your work. You can concretely use this guide to enrich an impact case, for instance.
Please use this indicator framework as a source of inspiration, not as a checkbox system or a competition who checks the most boxes. The indicators should fit your work and narrative.
Support for you and your team in using these tools is available!
Internal Support Overview
Contact
At BMS, Tom Boogerd is the main contact point for any impact-related questions, workshop requests or when you have ideas you wish to share (feel welcome!).

Internal Support Offer
The table below tries to match more specific support needs to internal UT support offer:
Support need | Where to go |
|---|---|
I want to know more about science communication and/or Citizen Science | Workshop Fundamentals of Science Communication and Citizen Science |
I am interested in Citizen Science and want support in involving citizens in my work | |
I am interested in Open Science, and wish to connect to colleagues with the same passion | |
I want to work on my visibility and brand as a scientist | Workshops Personal Branding for Scientists or Workshop Effective Outreach |
I want a sparring partner for a communication strategy, I want a sparring partner for general (internal) communication challenges | Contact Corjan van der Kuil (Marketing & Communication BMS) |
I want someone to proofread my communication efforts (e.g., for outreach activities) | Writing centre of the UT Language Centre |
I wish to transfer my work to relevant stakeholders (in a general sense: upscaling, licensing, or in a business sense: spin-off, copyrights, patents) | Knowledge Transfer Office of the UT, located at Novel-T |
I want to make a nice video, make use of the do-it-yourself-studio, get a photographer, or make a podcast | |
I want to compose a media plan or work on a press release | |
I want a social media plan, get social media analytics, or submit material to UT social media |
Impact Glossary
Impact pathways, valorisation, 4th generation university... There are quite some terms you can hear in conversations around impact (and read on the BMS Position Paper on Impact). The Impact Glossary provides some definitions of key terms. Are you missing a term? Let us know.
More Tools and Resources
In addition to the Impact Cases template and the Impact Indicator Guide above, there are many interesting and inspiring tools and resources on the topic of impact. Here is a short (incomplete) list, if you have any tools or resources you enjoy using, let us know!
- For inspiration and more background, check the micro lecture series from the NWO on “Working with an Impact Plan"
- Have a look at the Impact Helper from University of Oulu which helps you plan for impact by using a small worksheet
- The Impact Toolkit of University of Dublin is a comprehensive website that explores the concept of impact