In this master assignment you perform a design optimization on a flexure-based mechanism.
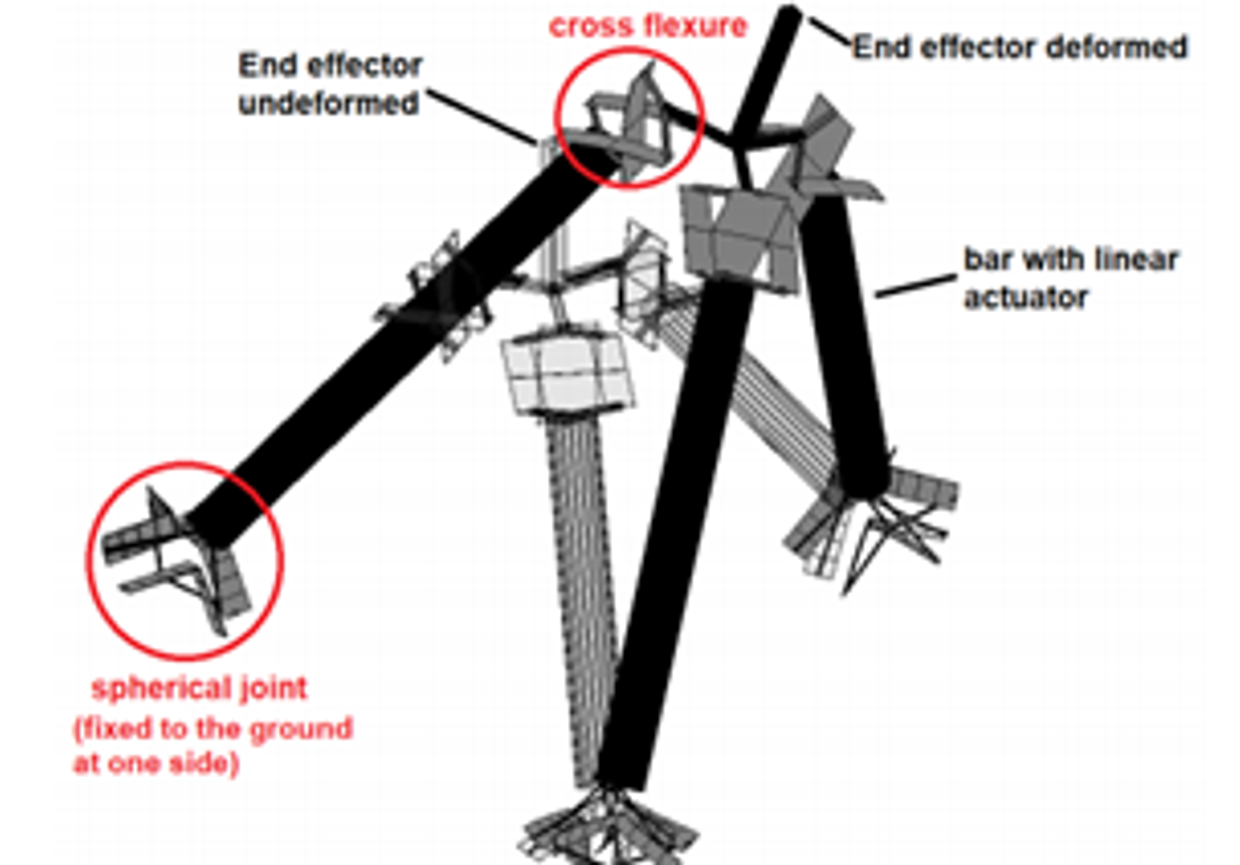
In design optimization, we want to choose the best dimensions of a mechanism in order to optimize some design criterion (e.g. large stiffness in supported directions) under some restrictions (e.g. maximum allowable stress). Design optimization is a great tool in designing but it has a major drawback: the optimization takes a lot of computation time. Therefore the optimization of complex mechanisms can take several days or is even unfeasible. The basic principle of design optimization is that many possible designs are evaluated and the best performing design is selected. To do this, the design criterion and the restrictions have to be obtained for each design in multiple deformed configurations. (The figure below shows an example of a flexure based mechanism in a deformed configuration, it is actuated by a linear actuator in each of the three bars.) Obtaining these configurations is the most time consuming part of design optimization.
Last year, a new method is found to obtain an approximation of these deformed configurations, which is faster than conventional methods to obtain deformed configurations. One of the key principles of this new method is that some pre-knowledge of the flexure joints is used. The figure shows a flexure based mechanism that contains six flexure joints: three cross flexures and three spherical joints. The new method can obtain a deformed configuration very efficiently by using some specific knowledge of these six joints. Using this new method in design optimizations makes the evaluation of a single design faster. However, the new method only gives an approximation of the deformed configuration. It is not clear whether these approximations are sufficiently accurate to be useful in design optimizations. The goal of the assignment is to investigate whether the approximated configurations are sufficiently accurate to be used in design optimizations.
The following tasks are foreseen:
- Define the optimization problem: define a suitable flexure based mechanism (or multiple mechanisms), define a design criterion and restrictions
- Run the optimization, computing the deformed configurations with the conventional way, i.e. with the multibody program SPACAR.
- Run the optimization, using the new method to compute the deformed configurations.
- Compare the optimization results in terms of efficiency (i.e. computation time and number of iterations in the optimization loop) and in terms of accuracy (i.e. how well does the optimal design perform?)