Duration
Start: 01-04-2017
End: 31-03-2021
Partners
Staff
Description
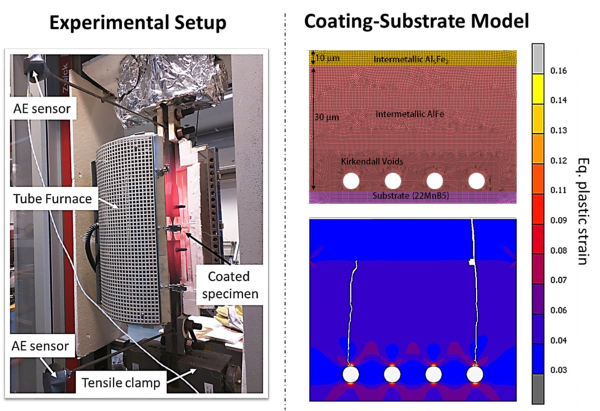
For industrial hot stamping applications, press hardening steel is usually coated with Al-10wt.%Si, in order to prevent substrate decarburization and oxidation at elevated temperatures. However, during hot stamping, the AlSi coating layer fractures, causing severe tool wear, substrate oxidation and increased friction coefficient between the tool and stamped part. The initiation of coating fracture can largely be attributed to the formation of several Fe-Al intermetallic compounds via Fe-diffusion, which also results in void formation throughout the coating layer. These intermetallics are formed mainly during the heating stage, with decreasing Fe‑content from the coating‑substrate interface. Due to distinctive thermo mechanical properties of intermetallics compared to the steel substrate, the interaction between different intermetallics, including voids, causes high strain localization around the voids, leading to coating fracture. The aim of this project is to detect the initiation of cracks in the coating layer at hot stamping conditions and develop a thermo-mechanical fracture indicator model of the coating-substrate system.


