Lifetime and degradation behaviour of PTFE coolant hoses

Chris-Jan Bolks - (March 2025)
Link to thesis: https://purl.utwente.nl/essays/105274
SUMMARY
PTFE coolant hoses used in radar systems for naval environments (Fig. 1) are expected to have a long service life, but their actual degradation behaviour and failure mechanisms remain uncertain. To ensure system reliability and optimize maintenance strategies, it is essential to understand how these hoses degrade over time under operational conditions.
This research investigates the degradation mechanisms and lifetime prediction of PTFE coolant hoses (Fig. 2) used in Thales radar systems. Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) and Fault Tree Analysis (FTA) were performed to systematically identify failure causes and risks. A combination of experimental and analytical methods was applied, including Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM), Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC), hardness testing, tensile testing, burst pressure testing and thermal aging experiments. PTFE hose samples were thermally aged using accelerated temperature testing equipment, reaching a maximum aging setpoint of 250 °C for 24 days.

Figure 1: Thales Radar on a navy frigate
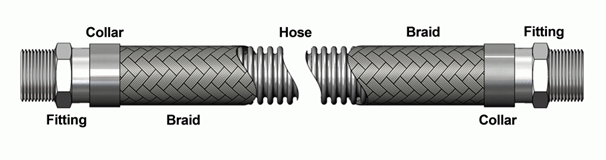
Figure 2: Industrial hose construction
A lifetime prediction model was developed to estimate hose durability based on material degradation trends. The findings contribute to improved failure predictability and enable informed decisions regarding maintenance and replacement strategies.
KEY RESULTS
· Failure analysis using FTA (Fig. 3) and FMEA resulted in the identification of key degradation mechanisms and failure pathways.
· Tensile test results, visualized in a cloud point plot, provided a general overview of the material's mechanical degradation over time (Fig. 4).
· SEM analysis of a reference hose (10-yrs in operation) revealed surface cracks, indicating potential failure initiation points (Fig. 5).
· Hardness tests confirmed changes in thermal and mechanical properties, linking them to material aging.
· A lifetime prediction model was established (Fig. 6), correlating degradation data with operational conditions to estimate hose service life (see Table 1). With key limitations known, this predicted lifetime could be used to re-evaluate the preventive replacement policies of Thales
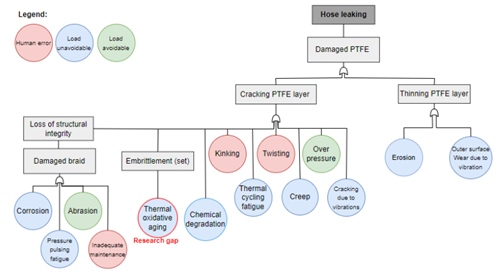
Figure 3: Fault tree analysis for hose failures
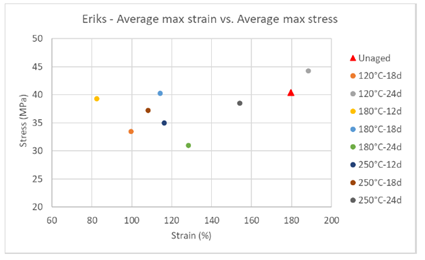
Figure 4: Stress-Strain plot unaged and aged PTFE hose samples
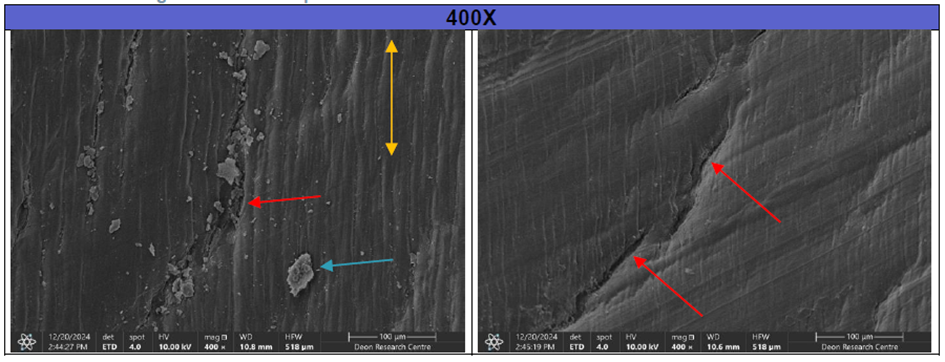
Figure 5: SEM results 400x; Reference hose 10-yrs operation
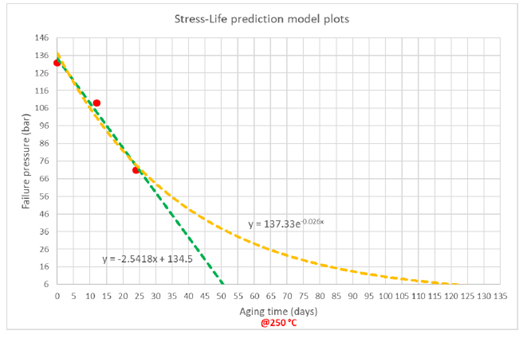
Figure 6: Lifetime prediction model
Table 1: Lifetime prediction for linear and exponential models
