Bachelor Assignment
Pose correction for 2D face recognition
Type: Bachelor EE
Student: Unassigned
Duration: TBD
Supervisors:
Introduction
Biometrics is about recognising persons based on their physical properties, behaviour or traces they leave. Examples of biometric modalities are face, ngerprint, iris, voice etc. In 2D face recognition, the main challenges are variation in pose, illumination and expression and to a lesser extent age and resolution. The latter two refer to the comparison of facial images of the same subject but with different age and low resolution recordings. Pose is one of the largest challenges, because the appearance of the face changes dramatically depending on the viewing direction. At DMB, we develop our own face recognition system and handling pose is a very important step in the whole process.
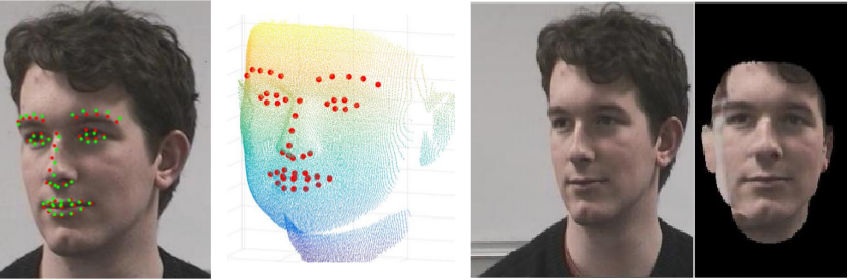
Assignment
One way to handle pose is to design a pose correction method that will transform the face image to a frontal view (see gure on the right). There are numerous ways to realise this, but one approach is to detect a number of landmarks on the image (see gure left). If the landmarks are also available on a (general) 3D face model, we can first estimate the pose using the landmarks and next determine a transformation to a frontal image (which is easy in 3D). Some students have designed a first implementation based on this approach, which looked promising. This assignment includes extending their work to make it more robust and to handle artifacts that result from stretching and compressing image parts and self-occlusion. Furthermore, the method whould be tested in combination with face recognition software.



