Sustainable membranes with biological functionalities for advanced water treatment
LijieLi (PhD Candidate), Wiebe de Vos (promotor), Saskia Lindhoud (co-promotor) |
Duration: 2020-2024 |
Funding: CSC |
Introduction
Membrane technology plays an important role in many fields, including agriculture, industry, and medicine. An aqueous phase separation (APS) approach has been successfully developed to prepare synthetic polyelectrolyte complex membranes. This approach uses water as both solvent and non-solvent, which effectively eliminates the need for harmful organic solvents as required for the traditional nonsolvent-induced phase separation (NIPS) method. Compared to synthetic polyelectrolytes, natural polyelectrolytes possess the advantages of nontoxicity, biocompatibility, and biodegradability, and their membranes can also be applied to extensive fields like synthetic membranes to remove harmful chemicals and particles from polluted water. Therefore, it is promising to prepare more sustainable natural polyelectrolyte membranes through the aqueous phase separation approach. Moreover, different enzymes could be introduced to prepare membranes with biological functionalities, which will be used in water treatment fields.
Keywords
membranes, polyelectrolyte complex, aqueous phase separation, enzyme, bio-catalytic activity
Technological challenges
The aqueous phase separation method has been used to prepare synthetic polyelectrolyte membranes. However, these synthetic polyelectrolytes are still fossil-based, which is not totally sustainable. The aim of this work is to prepare more sustainable natural polyelectrolyte membranes with biological functionalities through the aqueous phase separation approach.
Research goals
This research will focus on (i) preparing natural polyelectrolyte complex membranes through aqueous phase separation and (ii) introducing enzymes to prepare membranes with biological functionalities, and used for water treatment.
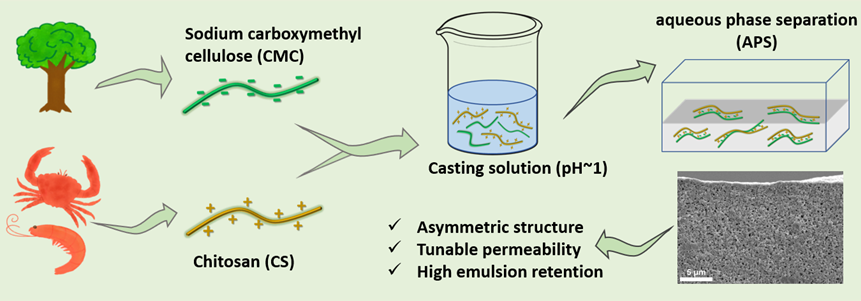
Picture derived from: Li, L., Baig, M.I., de Vos, W.M., Lindhoud, S., Preparation of Sodium Carboxymethyl Cellulose–Chitosan Complex Membranes through Sustainable Aqueous Phase Separation. ACS Applied Polymer Materials, 2023.
