Strong airflows in the lower atmosphere, so-called ‘low-level jets’, have an impact on the performance of wind farms. The height at which this jet moves, makes the difference: does it flow above the turbines, at the level of the turbines or even below? This determines if all turbines benefit from it, or just the front row, researchers of the University of Twente demonstrate in their paper in the Journal of Renewable and Sustainable Energy.
Wind turbines, responsible for growing share of our ‘energy mix’, have increased in height over the years: the early generations had heights of 50 meter and below, the latest generation exceeds heights of 250 meter, with rotor blades of over 100 meter in length. Effects that are seen in boundary layers in the lower atmosphere, typically at heights between 50 and 1000 meter, start playing an important role. For smaller wind turbines, these effects typically take place above the wind turbine, while for the current sizes, they can play a role at the level of the turbine or even below that. The ‘rivers of air’, called low-level jets (LLJ’s), were observed at many places in the world including the North Sea region, home to many windfarms.
Researchers Srinidhi Gadde and Richard Stevens did extensive computer simulations on a wind farm consisting of 40 turbines, four by ten, to study the effect of LLJ’s on the performance. Earlier research showed that the wake of each turbine influenced the next turbine in the row. This wake also plays an unexpected role in attracting the low-level jet.
Harvesting extra energy
In case the jet flows in the direction of the wind farm, at the level of the wind turbines, it is just the first row of turbines that benefits from it: it has no effect on the turbines further downstream. If the jet is above the wind turbines, however, the turbulent flow behind each turbine causes the jet moving down. Extra energy is harvested by the wind farm as a whole. The most remarkable effect takes place at jets flowing below turbine level: these jets are pushed upward by an effect called negative wind shear, resulting in higher levels of energy for turbines further downstream.
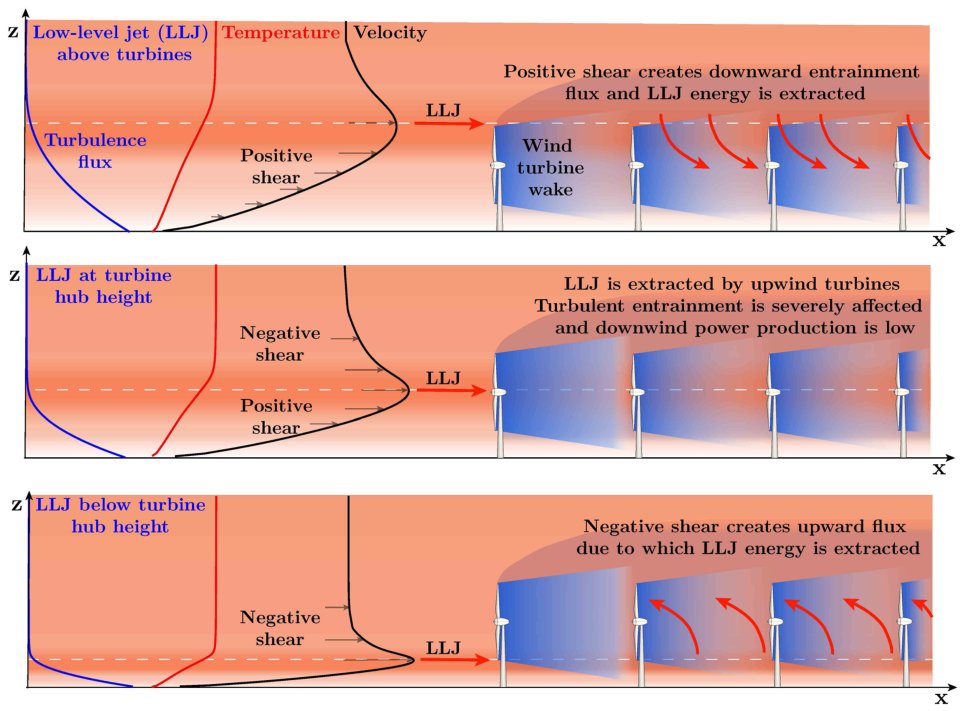
Three situations. In the upper figure, the jet is above the wind turbines. It is pulled down, so the turbines further downstream also harvest extra energy. In the figure in the middle, the jet is at turbine level. Only the first row of turbines benefit, there is no effect on the turbines downstream. The lower figure shows a jet that is below the turbine, this is pulled upward by the interaction of wake (blue) and wind shear; the turbines further downstream benefit.
Land and sea
These new insights can help designing the wind turbines and positioning them in a wind farm. Further research will have to shed light on effects caused by the shape of coastal regions and temperature variations associated with it.
The research was done in the Physics of Fluids group of the University of Twente. It is part of the ‘Computational Sciences for Energy Research’ programme of Dutch Research Council NWO and Shell.
The paper ‘Effect of low-level jets height on windfarm production’, by Srinidhi Gadde and Richard Stevens, is in the latest edition of the Journal of Renewable and Sustainable Energy (JRSE), an American Institute of Physics publication.





