RĔGO brings together top academic and industrial experts from Europe to develop micro-robot swarms designed for complex, human-centered tasks in various industries.
RĔGO, short for Cognitive Robotic Tools for Human-Centered Small-Scale Multi-Robot Operations, envisions micro-robots that can work together—either autonomously or with human guidance—on intricate tasks requiring precision and teamwork. These tiny robots are expected to impact healthcare, environmental sustainability, and industrial automation greatly.
"The potential for these micro-robot swarms is limitless," says Dr. Claudio Pacchierotti, project coordinator. "With RĔGO, we’re pushing the boundaries of human-robot collaboration, enabling humans to seamlessly control multi-robot systems at the microscale and targeting some of the robotics toughest challenges."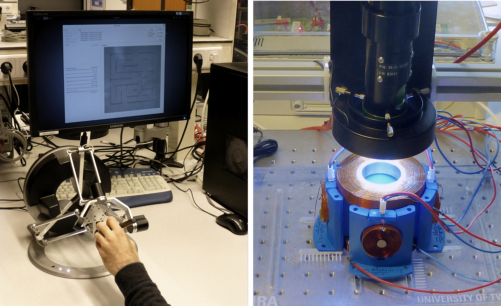
A human user controls the motion of a microrobot via a sensory feedback interface, bridging the gap between macro and micro-scale interaction.
RĔGO’s main focus areas
1. Modular, Adaptable Micro-Robots: These small robots will be versatile enough for various uses, from precise surgeries to cleaning up environmental hazards.
2. AI-Driven Swarm Coordination: Using AI, the robots will split tasks among themselves in real-time, ensuring smooth teamwork on complex challenges.
3. Human-Robot Teamwork: With user-friendly interfaces, human operators can easily control the robots using rich sensory feedback—sensing and reacting to the surroundings as they guide the robots.
4. Sustainability: In line with the European Green Deal, RĔGO is looking into green materials and energy-saving designs, allowing the robots to be used in sustainable projects like managing pollution and cleaning water.

Where Will These Micro-Robots Be Used?
RĔGO has broad potential and could change multiple industries:
Healthcare: Micro-robots could revolutionize surgeries and medical treatments by enabling precise drug delivery and targeting cancer in a minimally-invasive fashion.
Environmental Sustainability: These robots could play a role in cleaning up pollution, managing waste, and even treating water.
Industrial Automation: In fields such as electronics and precision manufacturing, micro-robots can play a vital role in assembling tiny components that are difficult or impossible for humans to handle.
More information
RĔGO is led by CNRS (France) and involves partners from four EU member countries collaborating to achieve a scientific breakthrough in the field of human-robot interaction for micro-robotics. These partners are CHU Rennes (France), Italian Institute of Technology (Italy), Haption (France), Scuola Superiore Sant'Anna (Italy), Inria (France), Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf (Germany) and the University of Twente.
This week the Surgical Robotics Laboratory of the UT, led by Prof. Dr. Sarthak Misra, is hosting the consortium of project RĔGO to coordinate the scientific work for the next few years. The RĔGO project is a Research and Innovation Action (RIA) funded by the European Union’s Horizon 2020 program (Grant Agreement 101070066) which creates Small AI-powered robots for a new future. Further information related to the RĔGO project is available on the project’s website. Additionally, you can reach us via our social media accounts: LinkedIn and Twitter.






