- Jinfeng Mu - PhD student
- Sonia García Blanco - Scientific Staff
- Mustafa Akin Sefunc - Former member
The aim of this project is to develop Er3+ doped photonic wire amplifiers integrated on two of the most promising passive generic integration platforms currently proposed for very large photonic integration, TriPleXTM and silicon-on-insulator (SOI). The material proposed for the amplifier is a potassium double tungstate doped with erbium ions. The high absorption and emission cross-sections of erbium ions in this host material, together with a potentially high erbium concentration and the very high electromagnetic field confinement in the small waveguide cross-section of the photonic wires will enhance the achievable gain per unit length. The amplifiers will be integrated onto TriPleXTM and SOI photonic motherboards.
Bonding and transfer techniques will be developed in this project to permit the transfer of a thin layer of amplifier material onto a passive photonic substrate. This thin layer will then be used to fabricate the photonic wire amplifiers. Low loss coupling schemes to bring both the optical pump and signal to the on-chip amplifier will be developed. High-speed amplification (>Tbps) on a photonic wire amplifier providing a total gain similar to a typical EDFA (10-20 dB), very low noise figure, at a device length of merely a few millimeters and consuming 2-3 mW of pump power will be demonstrated. The proposed amplifiers will constitute a very important milestone towards the practical utilization of photonics in on-chip optical networks.
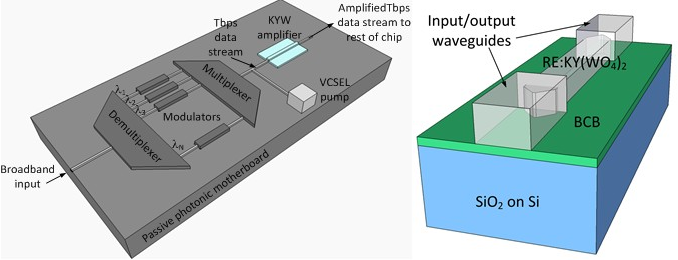
Fig. 1| (a) Er3+ doped KYW amplifier onto a passive nanophotonic circuit; (b) proposed photonic wire structure with input/output dielectric waveguides.
Articles
The following articles have been published regarding this project:
2017
Mu, J., Dijkstra, M., Yong, Y. S., Segerink, F. B., Worhoff, K., Hoekman, M., ... García Blanco, S. M. (2017). Low-loss, broadband and high fabrication tolerant vertically tapered optical couplers for monolithic integration of Si3N4 and polymer waveguides. Optics letters, 42(19), 3812-3815. DOI: 10.1364/OL.42.003812
Mu, J., Dijkstra, M., De Goede, M., Yong, Y. S., & García-Blanco, S. M. (2017). Ultra-low-loss and broadband mode converters in Si3N4 technology. In Integrated Optics: Devices, Materials, and Technologies XXI (Vol. 10106). [101060R] SPIE. DOI: 10.1117/12.2252706
2016
Mu, J., Vázquez-Córdova, S. A., Sefünç, M., Yong, Y. S., & García Blanco, S. M. (2016). A low-loss and broadband MMI-based multi/demultiplexer in Si3N4/SiO2 technology. Journal of lightwave technology, 34(15), 3603-3609. DOI: 10.1109/JLT.2016.2578463
Mu, J., Sefünç, M., Xu, B., Dijkstra, M., & García Blanco, S. M. (2016). Design and fabrication of adiabatic vertical couplers for hybrid integration by flip-chip bonding. In J-E. Broquin, & G. N. Conti (Eds.), SPIE Proceedings vol 9750, Integrated Optics: Devices, Materials, and Technologies XX 975012 (pp. 975012-1-975012-10). San Francisco, CA, USA. DOI: 10.1117/12.2212206
Sefünç, M., Alexoudi, T., Mu, J., Dijkstra, M., & García Blanco, S. M. (2016). Fabrication of high-contrast waveguide amplifiers in erbium doped potassium double tungstates. Paper presented at 18th International Conference on Transparent Optical Networks, ICTON 2016, Trento, Italy.DOI: 10.1109/ICTON.2016.7550527
Mu, J., Alexoudi, T., Yong, Y. S., Vázquez-Córdova, S. A., Dijkstra, M., Worhoff, K., ... García Blanco, S. M. (2016). Low-loss highly tolerant flip-chip couplers for hybrid integration of Si3N4 and polymer waveguides. IEEE photonics technology letters, 28(23), 2748-2751. DOI: 10.1109/LPT.2016.2616021
Mu, J., Dijkstra, M., Yong, Y. S., Vázquez-Córdova, S. A., & García Blanco, S. M. (2016). Low-loss multimode flip-chip couplers for the hybrid integration of Si3N4 and polymer waveguides.
2014
Mu, J., Sefünç, M., & García Blanco, S. M. (2014). Design and length optimization of an adiabatic coupler for on-chip vertical integration of rare-earth-doped double tungstate waveguide amplifiers. In 16th International Conference on Transparent Optical Networks (ICTON), 2014 (pp. 1-4). Graz, Austria: IEEE. DOI: 10.1109/ICTON.2014.6876570
