Looking for a bachelor or master assignment? Please contact us for the possibilities in the Department of Membrane Science & Technology. Below you will find our vacant student assignments.
- Sustainable green membranes by eBeaming polyelectrolytes
Background
Membrane processes can significantly contribute to achieving the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (e.g., 3, 6, 7, 12, 13) and are crucial for fundamental processes, e.g., water treatment and medical applications. However, membranes are mainly made from fossil-based raw materials using hazardous solvents. These membranes have unique properties (separation characteristics, mechanical stability), important for their respective applications making it challenging to replace them with more sustainable materials and fabrication procedures.Polyelectrolytes are a promising replacement for conventional membrane materials. Water can be used as the solvent for polyelectrolyte membrane fabrication, replacing hazardous organic solvents like NMP and DMF. Furthermore, bio-based polyelectrolytes can replace fossil-based raw materials. However, achieving the same separation characteristics and especially mechanical stability as fossil-based membranes is still a challenge.
Hence, this master’s thesis focuses on developing a new membrane fabrication method using an electron beam treatment for polyelectrolyte membranes to enhance the mechanical stability and potentially the membrane’s porous structure and, thus, the separation characteristics.
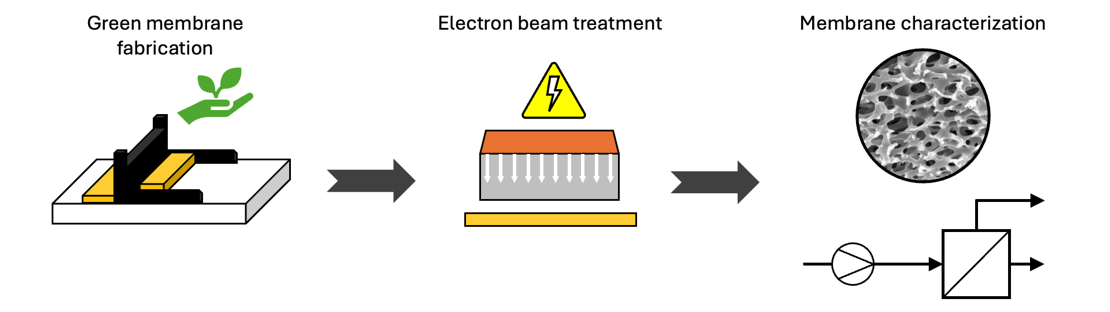
The work mainly focuses on:
- Screening of bio-based polyelectrolytes suitable for membrane fabrication.
- Fabricating bio-based polyelectrolyte membranes on lab-scale.
- Development of an electron beam post-treatment procedure for polyelectrolyte membranes.
- Characterizing membranes regarding their morphology, mechanical stability, and separation characteristics.
This assignment is suitable for both bachelor’s and master’s students.
If you’re interested and would like to know more about this project, contact Stefan Herrmann (s.herrmann@utwente.nl).
- Fabrication of reinforced saloplastic ion exchange membranes
Hestie Brink, Saskia Lindhoud, Wiebe de Vos, University of Twente
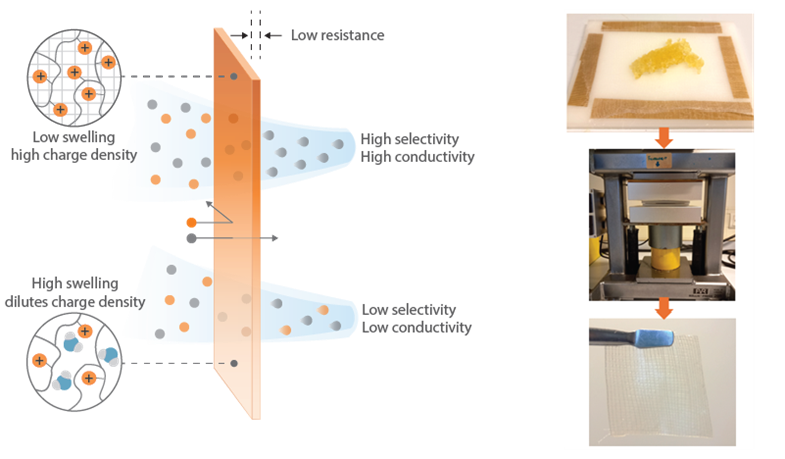
Ion exchange membranes (IEMs) are essential components for the efficient operation of a wide range of electrochemical technologies, including electrodialysis, water electrolysis, and fuel cells.1 These non-porous membranes contain a high concentration of fixed charges, which enables the separation of ions based on their charge. Within electrochemical cells, IEMs act as separators between the anode and cathode compartments and are used to regulate the transport of ions based on charge exclusion. IEMs are mainly evaluated based on their ionic resistance and permselectivity, which affect the energy intensity and efficiency of these processes.2 The harsh operating conditions required for specific applications also make chemical stability an important parameter to consider. Consequently, there is a growing need to develop highly conductive membranes that are stable in extreme pH and oxidative environments.
It has recently been demonstrated that sustainable and highly stable ion exchange membranes can be produced through the hot-pressing of non-stoichiometric polyelectrolyte complexes, resulting in so-called saloplastic membranes.3 This simple approach facilitates the fabrication of IEMs using saltwater, thereby eliminating the reliance on toxic solvents typically associated with conventional membrane production methods. Furthermore, saloplastic materials are recyclable which further highlights the sustainability of this approach.
The objective of this project is to enhance the performance of saloplastic anion exchange membranes through reinforcement. By hot-pressing a mesh into the IEM, a thin yet mechanically stable freestanding film can be produced that will minimise the resistance of the membrane. Moreover, the incorporation of hydrophobic mesh materials could potentially reduce membrane swelling, leading to significant improvements in the fixed charge density, and thus membrane performance.
This assignment can be suitable for either bachelor and master students.
If you want to know more about this project, please contact Hestie Brink (h.a.brink@utwente.nl).
References
[1] Ran, J. et al. Journal of Membrane Science 2017, 522, 267-291.
[2] Kitto, D.; Kamcev, J. Journal of Membrane Science 2023, 677, 11-20.
[3] Krishna, A.B. et al. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 2021, 593, 11-20. - Developing Dense Polyelectrolyte Multilayer Membranes for organic micropollutant removal
Background:
Organic micropollutant (OMP) contamination in water, such as pharmaceuticals, pesticides, and personal care products, is an emerging concern for global water treatment efforts. Although present in trace amounts, these OMPs can be harmful even at very low concentrations. Due to their small molecular sizes, many existing filtration technologies struggle to remove them from water sources effectively. As water scarcity intensifies due to population growth, industrial activities, and climate change, the need for advanced filtration technologies becomes crucial.
Polyelectrolyte Multilayer (PEM) membranes, constructed by alternating layers of positively and negatively charged polyelectrolytes, exhibit unique properties such as tunable pore size, surface charge, and permeability. Current PEM membranes are either highly selective for OMPs or exhibit strong stability, but achieving both simultaneously remains a challenge. This project aims to develop membranes that balance high selectivity and stability to improve overall performance. This project aims to develop dense and stable PEM-based nanofiltration (NF) membranes for surface water treatment by testing novel polyelectrolyte pairs. Additionally, the membranes will be evaluated for their stability and performance in harsh conditions, ensuring they maintain their selectivity and efficacy against micropollutants even after repeated use, leveraging their advanced properties to improve water purification efficiency.
Keywords: Polyelectrolyte multilayers, nanofiltration, dense membranes
During this project, you will focus on:
- Conducting an in-depth review of current literature on PEM membranes, focusing on their working mechanisms, properties, and efficacy in water treatment applications. This review will cover key topics such as the properties of different polyelectrolytes, their ion selectivity behavior, and the latest innovations in PEM membrane technology.
- Fabricate PEM membranes using the layer-by-layer technique, focusing on dense membrane formation to enhance treatment efficiency.
- Performing experiments to evaluate the permeability, salt retention, MP retention, and molecular weight cut-off (MWCO) of PEM membranes.
- Explore symmetric and asymmetric coating configurations for optimized membrane performance.
- Comparing the performance of dense PEM membranes with conventional NF membranes, focusing on improvements in selectivity.
This project is ideal for master's students seeking hands-on experience in advanced water treatment technologies.
For more information, please contact: Sina Rezaei (Sina.rezaei@utwente.nl)
- Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) for specific ion selective membranes
Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) are a class of porous hybrid materials that are composed of coordinated metal atoms that are linked to each other via organic linker molecules. This forms porous materials with pores in the order of magnitude of several Angstroms. This property makes MOFs interesting to use as a membrane to separate specific ions from each other, unlike conventional ion-exchange membranes which are primary based on charge-exclusion and show very limited ion-ion selectivity.
Relatively recently, in the field of ion separations in water MOFs became of interest for specific water treatment that needs to target specific types of ions in water that also consists of other less interesting ions that do not need to be removed. Due to these small pore sizes, ions that are transported through the membrane have to dehydrate some shells of water to fit into the MOF pores. Therefore MOF based membranes can separate ions based on how easy they lose their water shells[1,3]. This makes it possible for instance to recovery lithium ions selectively from a saline feed stream and it is possible to create a membrane that is more selective towards monovalent ions compared to multivalent ions (Cl- vs. SO4- or Na+ vs Mg2+) [1,2]. Furthermore it was found specifically for fluoride ions, that specifically bind fluoride to the MOF structure also enhanced the transport through a MOF membranes [3].
In this project we will make MOF modified membranes and will characterize the membrane for instance with SEM and XRD. Furthermore we will analyze the modified ion transport through the MOF membrane with bi-ionic potential measurements and finally we can potentially test how well this membrane works in an electric-driven separation processes to separate specific ions. This project has industrial implications into developing new resource recovery processes in industry of valuable components, such as lithium from seawater.
This assignment can be suitable for either bachelor or master students.
If you’re interested and would like to know more about this project, then don’t hesitate to contact Jeff Wood (j.a.wood@utwente.nl).
[1]: J. Lu et al. Efficient metal ion sieving in rectifying subnanochannels enabled by metal–organic frameworks. Nature Materials 2020 p. 767-774.
[2]: H. Zhang. Ultrafast selective transport of alkali metal ions in metal organic frameworks with subnanometer pores. Science Advances 2018 vol. 4 (2).
[3]: X.Li. Fast and selective fluoride ion conduction in sub-1-nanometer metal-organic framework channels. Nature Communications 2019 vol. 10 (1).
- Effect of a temperature & concentration gradient on the transport of ions through ion selective porous media
Previously, we have researched the influence of temperature gradients on the performance of electrodialysis experimentally [1,2] as well as numerically with a model system of ion selective nanochannels [3]. It was found that temperature differences can increase current at a given voltage (as expected from conductivity) and more interestingly that ion selectivity could be tuned based on these temperature differences due to variation in how the hydrated radius of ions change at different temperatures.
However, in an electrodialysis process, the salt concentration changes along the length of the membrane due to the electrical field, which drives the ions through the ion-exchange membrane. Therefore, more fundamental research into the effect of temperature and concentration gradients on the transport rate of ions through a membrane is necessary to exploit these effects.
In this work, we plan to study ion and related transport phenomena through a bed packed with ion-exchange resin particles, while keeping the temperature gradient and concentration gradient nearly constant across the bed. Ion exchange resin particles are composed of charged groups and therefore will preferentially allow the transport of counterions through the bed, while co-ions are retained by the ion exchange resin, which mimics a ion-exchange membrane. This setup allows to study the effect of concentration difference, electrical field strength, etc. on the rate of transport of different ions through porous ion exchange beds. This then has possible implications in how to improve industrially scale ion-exchange processes using low-grade waste heat.
This assignment can be suitable for either bachelor and master students.
If you’re interested and would like to know more about this project, then don’t hesitate to contact Jeff Wood (j.a.wood@utwente.nl).
[1]: A. Benneker et al. Effect of temperature gradients in (reverse) electrodialysis in the Ohmic regime. Journal of Membrane Science 2018 p. 421-428.
[2]: A. Benneker et al. Influence of temperature gradients on mono- and divalent ion transport in electrodialysis at limiting currents. Desalination 2018 p. 62-69.
[3]: A. Benneker et al. Influence of temperature gradients on charge transport in asymmetric nanochannels. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics 2017 vol. 19 (41).
- Characterization of physicochemical changes in membranes in the valorization of food waste
Are you interested in contributing to the reduction of food waste? Do you like to understand how the chemistry and properties of membranes change when exposed to different environments? Then this project is for you.
Food systems are responsible for one third of the greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions (Crippa et al. 2021) and in the current food production systems 30-50% of food is wasted. To be able to feed the growing population (10 billion people by the decade of 2050 (United Nations 2022)) in a sustainable manner, recovering ingredients from food waste has become one of the priorities of governmental organizations and private companies, as most of this waste is perfectly edible and presents high nutritional value (e.g. proteins, sugars, etc.). The production of ingredients from food side streams is known as upcycling.
In this project, Greencovery and the Membrane Process Technology group of the University of Twente work together to understand how we can use membranes to reduce the energy consumption during the upcycling of food side streams. The project is part of a research consortium involving several companies (Recircanol: https://ispt.eu/projects/recircanol/).
During the standard upcycling process ethanol is recovered using traditional methods like evaporation and distillation. Implementing membranes would help to reduce the environmental impact and production cost of the process. However, the ethanol containing stream also has a high pH, which presents a challenge for traditional organic solvent resistant/tolerant nanofiltration membranes (Othman et al. 2010). Therefore, further research is needed to implement membranes in the solvent recovery step.
MSc student assignment
The objective of this assignment is to understand how the structures and properties of different commercially available nanofiltration membrane materials change when processing ethanol-water-hydroxide mixtures.
During the project you will perform the experiments, evaluate the obtained data and interpret the results. The assignment involves physicochemical characterization of the membranes using advanced techniques (like electronic microscopy (SEM), ellipsometry, streaming potential, chromatography). Also, you will develop your soft skills (time and stakeholders management, oral and written communication, independence and initiative).
The project will take place in the facilities of the Department of Membrane Science and Technology at the University of Twente.
This assignment is suitable for master students.
If you’re interested and would like to know more about this project, then don’t hesitate to contact Paco Caparros (f.caparrossalvador@utwente.nl).
- Crippa, M., E. Solazzo, D. Guizzardi, F. Monforti-Ferrario, F. N. Tubiello, and A. Leip. 2021. “Food Systems Are Responsible for a Third of Global Anthropogenic GHG Emissions.” Nature Food 2 (3): 198–209. https://doi.org/10.1038/s43016-021-00225-9.
- Othman, Rahimah, Abdul Wahab Mohammad, Manal Ismail, and Jumat Salimon. 2010. “Application of Polymeric Solvent Resistant Nanofiltration Membranes for Biodiesel Production.” Journal of Membrane Science 348 (1): 287–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2009.11.012.
- United Nations. 2022. “World Population Prospects.” Summary of results. New York. https://www.un.org/development/desa/pd/sites/www.un.org.development.desa.pd/files/wpp2022_summary_of_results.pdf.
- Evaluation of solvent-resistant NF membranes for the recovery of food ingredients
Are you interested in contributing to the reduction of food waste? Do you like to understand how the chemistry and properties of membranes change when exposed to different environments? Then this project is for you.
Food systems are responsible for one third of the greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions (Crippa et al. 2021) and in the current food production systems 30-50% of food is wasted. To be able to feed the growing population (10 billion people by the decade of 2050 (United Nations 2022)) in a sustainable manner, recovering ingredients from food waste has become one of the priorities of governmental organizations and private companies, as most of this waste is perfectly edible and presents high nutritional value (e.g. proteins, sugars, etc.). The production of ingredients from food side streams is known as upcycling.
In this project, Greencovery and the Membrane Process Technology group of the University of Twente work together to understand how we can use membranes to reduce the energy consumption during the upcycling of food side streams. The project is part of a research consortium involving several companies (Recircanol https://ispt.eu/projects/recircanol/).
During the standard upcycling process ethanol is recovered using traditional methods like evaporation and distillation. Implementing membrane technology would help to reduce the environmental impact and production cost of the upcycling process. However, the ethanol containing stream also has a high pH, which presents a challenge for traditional organic solvent resistant/tolerant nanofiltration membranes (Othman et al. 2010). Therefore, further research is needed to implement membranes in the solvent recovery step.
BSc or MSc assignment
The assignment's objective is to evaluate the behavior and performance of different commercially available (nanofiltration)membranes on laboratory scale (focusing on flux, rejection), and to determine the impact of these changes on the process design.
During the project you will perform the experiments, evaluate the obtained data and interpretate the results. Also, you will develop your soft skills (time and stakeholders management, oral and written communication, independence and initiative).
The project will take place in the facilities of the Department of Membrane Science and Technology at the University of Twente.
This assignment is suitable for both bachelor and master students.
If you’re interested and would like to know more about this project, then don’t hesitate to contact Paco Caparros (f.caparrossalvador@utwente.nl).
- Crippa, M., E. Solazzo, D. Guizzardi, F. Monforti-Ferrario, F. N. Tubiello, and A. Leip. 2021. “Food Systems Are Responsible for a Third of Global Anthropogenic GHG Emissions.” Nature Food 2 (3): 198–209. https://doi.org/10.1038/s43016-021-00225-9.
- Othman, Rahimah, Abdul Wahab Mohammad, Manal Ismail, and Jumat Salimon. 2010. “Application of Polymeric Solvent Resistant Nanofiltration Membranes for Biodiesel Production.” Journal of Membrane Science 348 (1): 287–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2009.11.012.
- United Nations. 2022. “World Population Prospects.” Summary of results. New York. https://www.un.org/development/desa/pd/sites/www.un.org.development.desa.pd/files/wpp2022_summary_of_results.pdf.
- CFD simulations to assess the influence of flow cell geometry on NF membrane performance
Are you interested in contributing to the reduction of food waste? Do you like to understand how the chemistry and properties of membranes change when exposed to different environments? Then this project is for you.
Food systems are responsible for one third of the greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions (Crippa et al. 2021) and in the current food production systems 30-50% of food is wasted. To be able to feed the growing population (10 billion people by the decade of 2050 (United Nations 2022)) in a sustainable manner, recovering ingredients from food waste has become one of the priorities of governmental organizations and private companies, as most of this waste is perfectly edible and presents high nutritional value (e.g. proteins, sugars, etc.). The production of ingredients from food side streams is known as upcycling.
In this project, Greencovery and the Membrane Process Technology group of the University of Twente work together to understand how we can use membrane technology to reduce the energy consumption during the upcycling of food side streams. The project is part of a research consortium involving several companies (Recircanol https://ispt.eu/projects/recircanol/).
During the standard upcycling process, ethanol is recovered using traditional methods like evaporation and distillation. Implementing membrane technology would help to reduce the environmental impact and production costs of the process. However, the ethanol containing stream also has a high pH, which presents a challenge for traditional organic solvent resistant/tolerant nanofiltration membranes (Othman et al. 2010). Therefore, further research is needed to implement membranes in the solvent recovery step.
BSc or MSc assignment
The objective of this assignment is to use computational fluid dynamics (CFD) to understand the impact of module configuration on the membrane performance (flux, rejection) and overall nanofiltration process when working with ethanol-water-hydroxide mixtures.
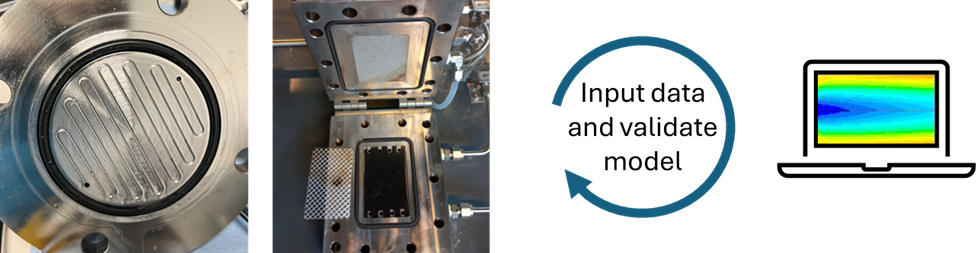
You will simulate chemical species transport and fluid flow patterns for different membrane cell geometries, compare the simulation results with experimental data, and interpretate the results. Also, you will develop your soft skills (time and stakeholders management, oral and written communication, independence and initiative).
The project will take place in the facilities of the Department of Membrane Science and Technology at the University of Twente.
This assignment is suitable for either bachelor or master students.
If you’re interested and would like to know more about this project, then don’t hesitate to contact Paco Caparros (f.caparrossalvador@utwente.nl).
- Crippa, M., E. Solazzo, D. Guizzardi, F. Monforti-Ferrario, F. N. Tubiello, and A. Leip. 2021. “Food Systems Are Responsible for a Third of Global Anthropogenic GHG Emissions.” Nature Food 2 (3): 198–209. https://doi.org/10.1038/s43016-021-00225-9.
- Othman, Rahimah, Abdul Wahab Mohammad, Manal Ismail, and Jumat Salimon. 2010. “Application of Polymeric Solvent Resistant Nanofiltration Membranes for Biodiesel Production.” Journal of Membrane Science 348 (1): 287–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2009.11.012.
- United Nations. 2022. “World Population Prospects.” Summary of results. New York. https://www.un.org/development/desa/pd/sites/www.un.org.development.desa.pd/files/wpp2022_summary_of_results.pdf.
- PEM membrane module design for micropollutant removal
Polyelectrolyte multilayer membrane module design: advancing micropollutant removal using a modular approach
Organic micropollutants (OMPs), such as pharmaceuticals, pesticides, and PFAS substances, pose significant environmental and health risks. Many OMPs are chemically stable, bio-accumulative, and do not degrade in conventional wastewater treatment processes. Addressing the issue of micropollutants has become an important topic to ensure water quality and safety.
Polyelectrolyte multilayer (PEM) membranes, constructed by the layer-by-layer assembly of alternating layers of positively and negatively charged polyelectrolytes, exhibit unique properties such as tuneable pore size, surface charge, and selective permeability. This makes them well-suited for the selective removal of OMPs.
Often, the performance of PEM membranes is evaluated using individual fibres. However, this approach does not accurately reflect the conditions in full-scale industrial applications, where membranes are used in modular configurations. Testing modules, rather than individual fibres, gives a more realistic assessment of membrane performance under operational conditions. It provides insights into module-level interactions, scaling behaviour, and overall system efficiency. This contributes to the development of more robust and efficient membrane systems.
The proposed project aims to design and test PEM membrane modules to explore their behaviour and performance. This approach is expected to provide a deeper understanding of the benefits and challenges associated with modular membrane design, particularly in the context of removing OMPs.
During this project, you will:
- Review the existing literature on PEM membranes, focusing on their mechanisms, properties, and the behaviour of different polyelectrolyte pairs.
- Learn and apply the techniques for fabricating PEM membrane modules in-house. This includes assembling modules with different polyelectrolyte pairs at varying module lengths and understanding the practical aspects of module construction.
- Characterize the modules by performing molecular weight cut-off (MWCO) tests using gel permeation chromatography (GPC).
- Gain proficiency in using the MExplorer cross-flow setup to test the fabricated modules, and utilize liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LCMS) to detect and characterize OMPs.
- Evaluate the micropollutant retention capabilities of the PEM membrane modules, beginning with spiked concentrations of OMPs in artificial surface and drinking waters, progressing to more realistic concentrations using real water sources.
- Compare the OMP removal efficiency of the modules based on membrane charge configurations (positive, negative, or half-positive-half-negative), evaluating both symmetric and asymmetric membranes to assess how membrane charge influences OMP removal.
- Investigate the impact of different operational parameters, such as transmembrane pressure and recovery ratio, on membrane performance. Analyse the fouling behaviour of membranes over longer (more realistic) running times.
Interested? Please contact Purvil Gangar (p.k.gangar@utwente.nl).
See also Design of novel charge-mosaic membrane processes (utwente.nl/mpt). - Removal of micropollutants from wastewater: pilot-scale investigation
Removal of micropollutants from wastewater: pilot-scale investigation
Background
Organic micropollutants (OMPs), such as pharmaceuticals, personal care products, pesticides and stimulants, appear in trace amounts (µg/l- ng/l) in wastewater and surface waters. These compounds are a source of concern for their persistent nature and impose environmental risks when introduced into the ecological environment. Because they are not sufficiently removed in most existing wastewater treatment facilities, there is a need to develop more efficient and cost-effective technologies to remove them.
Pilot installation
This research is conducted using a pilot-scale installation, located at the wastewater treatment plant (WWTP) in Enschede. The wastewater influent for the pilot is collected after the WWTP primary clarifier. The wastewater contains a spectrum of different pollutants, ranging from common (biodegradable) organic compounds to suspended solids, nutrients and pollutants like OMPs, PFAS, etc. Ideally, these compounds need to be removed from the water cycle for >80%.
The pilot is composed of a biological reactor, where most of the common pollutants are removed (e.g. COD, nutrients, etc.) through biodegradation with sludge. The sludge is separated from the water matrix through a clarifier. Most of the suspended particles are collected at the bottom of the clarifier and then recirculated back to the biological reactor, to keep control of the bio-activity in those reactors. The effluent stream from the clarifier is connected to a nanofiltration (NF) membrane installation. The NF membranes retain substantial part of the OMP’s (amongst other compounds). The NF permeate stream is discharged into the surface water. The NF concentrate stream, which contains the OMP’s, is returned to the biological reactor.
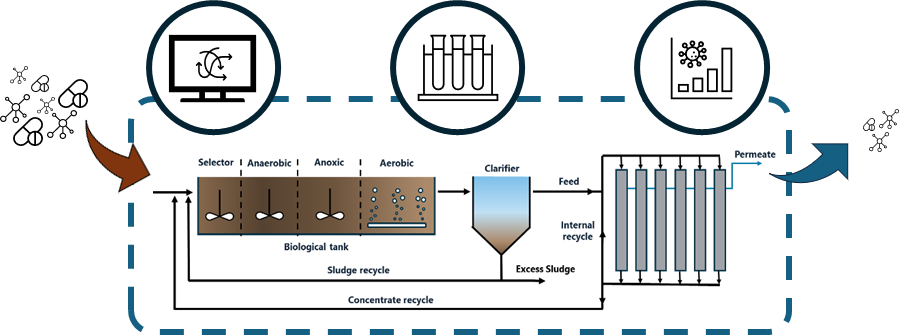
Objective
The main objective of this MSc assignment is to optimize the operation of the nanofiltration pilot, such that the extent of OMP removal in the wastewater treatment pilot is maximized. Obviously, the operation of the biology reactor should not be affected, and a stable membrane operation should be guaranteed. The content of the MSc assignment will be determined in more detail together with the student, but most likely will involve process monitoring, laboratory analyses and experiments, along with process optimization.
Interested? Please contact Mostafa Elshourbagy (m.m.a.elshourbagy@utwente.nl). See also Micropollutant removal using nanofiltration and concentrate recirculation (utwente.nl/mpt).
- Development of special RO membranes for brine concentration
Development and Characterization of Special RO Membranes for Brine Concentration
Highly saline (> 55 g/L) wastewater is produced by multiple industries [1]. The desalination industry alone produced more than 140 million m3 per day in 2019 [2]. Brine discharge is costly and has damaging effects on the environment [3]. Salts and water in the brine are valuable resources for recycling, and are wasted upon disposal. Therefore, it is desired to process brine to recover salt and water instead of discharging it. However, current thermal methods of brine separation are highly energy intensive [4]. Moreover, conventional membrane separation methods such as high pressure RO cannot be applied due to the excessively high pressures (>150 bars) required to overcome the osmotic pressure of the brine [5].
Osmotically assisted reverse osmosis (OARO) is an alternative technology that lowers the required pressures by providing salt solutions to both sides of the membrane [6] reducing the osmotic pressure difference over the membrane. This process will be used to split waste brine into concentrated and diluted streams. The dilute stream will then be processed into clean water, and the concentrated stream will be used as a source of salt. Thus, OARO will be explored as an alternative method for recovering water and salt from brine. The aim is to turn brine effluents into clean water and saturated salt solution (25 wt%), with an energy consumption lower than that of mechanical vapor recompression (<20 kWh/m3).
Master Thesis Assignment
Experimental studies have affirmed the applicability of OARO, but also showed that there is a significant loss in membrane flux under high salt concentrations [7,8]. A low flux negatively affects process economics. This MSc assignment focuses on evaluating commercial membranes under OARO conditions, and improving their characteristics through chemical treatments. The goal is to find those membranes and process conditions that minimize the energy consumption.
Emphasis is placed on the following aspects:
- Evaluating the water and salt fluxes of commercial membranes under OARO conditions, with varying salinity, pressure and crossflow velocity.
- Chemical treatment with alkylating agents, and characterization of the samples with zeta potential and FTIR spectroscopy measurements.
- Evaluating the water and salt fluxes of the treated membranes and comparison with the original membranes.
- Selection of the membrane and process conditions to model an OARO cascade.
Interested? Please contact Onur K. Aydın (o.k.aydin@utwente.nl).
See also Osmotically-assisted reverse osmosis (utwente.nl/mpt)References
- Panagopoulos A., Env. Sci. and Pol. Res., 29: 23736 (2022).
- Jones E. et al., Sci. of the Tot. Env., 657: 1343, (2019).
- Panagopoulos A. et al., Sci. of the Tot. Env., 693: 133545, (2019).
- Vane L. M., Journal of Chem. Tech. & Biotech., 92: 2506 (2017).
- Anvari A. et al., Desalination, 580: 117565, (2024).
- Bargeman G., Sep. Purif. Technol., 293: 121113, ( 2022)
- Togo, N. et al., Ind. & Eng. Chem. Res., 58: 6721, (2019).
- Turetta, M et al., Chem. Eng. Technol., 47: e202300553, (2024).
- Low salt rejection RO membranes for brine concentration
Characterization and development of low salt rejection RO membranes
for brine concentrationDue to reducing water availability and climate change, it is essential to minimize wastewater discharge and recover more freshwater. The reducing availability of water especially affects industry. Furthermore, the discharge of concentrated salt water disturbs aquatic ecosystems. Therefore it is essential to treat the brine properly[1]. In a zero-liquid discharge approach, this provides opportunities for recovering fresh water as well as making products such as crystalline salt from the saline waste stream.
Membrane-based technologies are very promising for brine treatment since they are more energy efficient than thermal concentration processes. However, conventional reverse osmosis (RO) cannot produce saturated brines due to limiting operating pressures (<150 bar) for conventional RO membranes. A possibility to overcome this pressure limitation is the use of low salt rejection RO membranes, which are also known as loose RO membranes [2] [3]. These membranes have a salt retention in between that for RO and NF membranes, which leads to a reduced osmotic pressure difference between concentrate and permeate [2]. As a result, the required transmembrane pressure is lower than that for RO membranes for a given concentration factor. Hence, LSRRO technology allows the production of concentrates with higher salt concentrations than achievable with conventional RO, which is why this technology is very promising. To evaluate and improve the process, membrane characterization and development is essential.
Master Thesis Assignment
In this MSc assignment, the focus is on characterizing commercial membranes under different salinities and pressures. Additionally, the effect of different impurities and impurity levels on the performance of the membrane will be determined. To evaluate the membrane performance, mainly water fluxes and solute retentions will be measured. Furthermore, to find the optimal membranes for the LSRRO process, modifying RO membranes using NaOCl, NaOH or H2SO4 will be considered to make them more loose. In the MSc assignment, emphasis is placed on the following aspects:
- Evaluating the retention and water and salt fluxes of commercial RO and NF membranes with varying salinity and pressure.
- Evaluating the effect of different impurities and impurity levels on the membrane performance.
- Chemical treatment of RO membranes and evaluating and comparing the modified membranes.
Interested? Please contact Lena S. Riechers (l.s.riechers@utwente.nl).
See also Low salt-rejection reverse osmosis (utwente.nl/mpt)References
- G. Bargeman, “Maximum allowable retention for low-salt-rejection reverse osmosis membranes and its effect on concentrating undersaturated NaCl solutions to saturation,” Sep Purif Technol, vol. 317, 2023, doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2023.123854.
- Z. Wang, A. Deshmukh, Y. Du, and M. Elimelech, “Minimal and zero liquid discharge with reverse osmosis using low-salt-rejection membranes,” Water Res, vol. 170, 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2019.115317.
- Y. Du, Z. Wang, N. J. Cooper, J. Gilron, and M. Elimelech, “Module-scale analysis of low-salt-rejection reverse osmosis: Design guidelines and system performance,” Water Res, vol. 209, 2022, doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2021.117936.
