3D Ultrasound image guidance of Radiofrequency Ablation of thyroid nodules
Radiofrequency ablation is a minimally invasive technique used for treating various diseases in the human body. Utilizing a frequency alternating current heat is generated that can destroy the target tissue. The focus for M3i is on liver and thyroid tumour ablation guided by ultrasound modalities.
PRINCIPAL RESEARCHER
Tim Boers
SUPPORT
Johan van Hespen
SUPERVISORS
Promotors: Srirang Manohar (M3I) and Michel Versluis (POF)
Co-promotor: Sicco Braak (ZGT)
FUNDED BY
ZGT CMS Wetenschapsvoucher
thyroid ablation
Evaluation and improvement of the benign thyroid tumour radiofrequency ablation therapy.
Motivation
Up to 68% of the population has a thyroid nodule (tumor), most of these are benign and cause no discomfort. However for some patients the nodule can grow too big resulting in symptoms, amongst others, swallowing and breathing difficulties as well as cosmetic complaints. Conventional treatment is surgical removal of the afflicted lobe, however minimally invasive options also exist. Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) is a minimally invasive technique used for treating various diseases in the human body. Utilizing a frequency alternating current heat is generated that can destroy the target tissue. The focus for M3i is on liver and thyroid tumor ablation guided by ultrasound modalities.
Benign thyroid tumor RFA is a treatment option introduced in the Netherlands late 2016 (first ablation was performed in South-Korea in 2002). Offering a very elegant and almost scar-free option for patients, albeit minimally invasive, it is not without risk. Using conventional 2D ultrasound the radiologist acquires a real-time view of the needle and a part of the nodule and ablation area. This results in two primary issues:
- The lack of 3D data results in inaccurate volume estimations, deviations of up to 25% are reported in literature, due to deviations in selection of the longest axis and its orthogonals. This impacts both diagnosis and perioperative settings. See also Figure 1A.
- The lack of 3D data results in a smaller field of view, which does not encompass the entire ablation area increasing the risk of complications and limits the possibilities for ablation planning and tracking, see also Figure 1B.
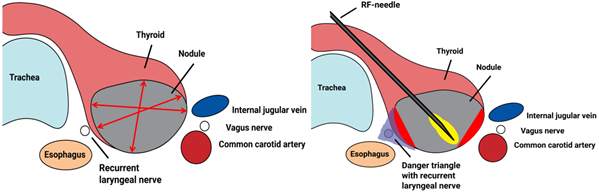
Figure 1: A (left), a schematic drawing of the thyroid and its relevant surrounding structures, what red arrow-line would be the longest axis here? B (right), a schematic drawing of an RFA procedure, illustrating the safetyzones (birght red areas) that need to be adhered to, as well as the lack of view on the other scanning directions.
Our solution is using real-time 3D ultrasound, this is possible with a matrix transducer, such as the one by Philips (see Figure 2). Being able to objectively measure the nodule volume may give a more accurate diagnosis as to what grade the thyroid nodule is. As well as giving a better baseline with which the follow-up scans after RFA can be compared. For the RFA, being able to make a pre-operative plan and track this plan during the intervention, with the same real-time 3D US imaging modality, may be a strong improvement for treatment efficacy and safety.

Figure 2: XL14-3 matrix transducer, by Philips Medical.
RATED multi-center study
As RFA is relatively new in the Netherlands we want to evaluate its current state and its impact on the quality of life of patients. To this end we set up a multi-center study wherein we ask patients to fill in a thyroid questionnaire asking them what the impact is of their thyroid disease as well as their current quality of life. This study was set up together with the ZGT and Rijnstate hospitals and includes Amsterdam UMC, Elkerliek and CWZ as centers as well.
Topics
- Radiofrequency ablation (RFA)
- Benign thyroid tumor
- Ultrasound (2D, 3D and real-time 3D)
- Deep learning
- Anthropomorphic phantom, see also the M3i page on phantoms
SECONDARY TOPICS
- Elastography (Shear wave, strain, acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI)
If you are interested in a master or bachelor assignment related to the above mentioned topics, please contact Tim Boers (t.boers@utwente.nl)
Collaborations
- Ziekenhuisgroep Twente (ZGT)
- Amsterdam UMC
- Rijnstate
- Elkerliek
- Canisius Wilhelmina Ziekenhuis (CWZ)
PRIZES
ZGT Wetenschapsdag onderzoeksprijs 2021
ZGT CMS Wetenschapsvoucher 2022 (50k€)
OPPORTUNITES
We need highly creative, industrious and passionate students to help us move the field further. The backgrounds required are in Biomedical Engineering, Applied Physics, Technical Medicine, and Computer Science. If you are interested in making an important contribution to this area, contact one the following:
PUBLICATIONS
Boers, T., Braak, S. J., Versluis, M., & Manohar, S. (2021). Matrix 3D ultrasound-assisted thyroid nodule volume estimation and radiofrequency ablation: a phantom study. European radiology experimental, 5(1), 1-10.

