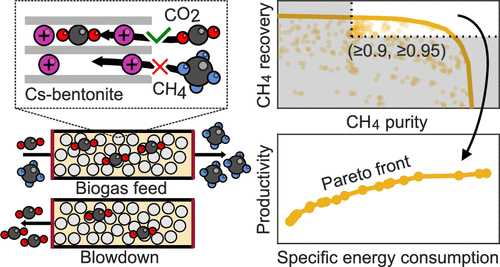
Biogas upgrading by vacuum-pressure swing adsorption involves the selective adsorption of CO2 over CH4 on a sorbent material to separate both components. This work assesses numerically the performance of the previously characterized Cs-exchanged bentonite clay for this separation (see https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.3c01635). This benchmarking study includes the effect of the process cycle configuration, the ambient temperature, the feed biogas composition, and the process operating parameters. A two-column unit operated at ambient feed pressure can upgrade 0.097 normal cubic meter feed biogas per kg sorbent per hour to a bio-CH4 product with a purity of 0.906 and with a CH4 recovery of 0.967 at a comparatively low specific energy consumption of only 0.072 kWh per produced normal cubic meter of CH4. The low bentonite cost, the comparatively low specific energy consumption due to the favorable linear CO2 adsorption isotherms, and the high recovery due to the high CO2/CH4 selectivity make Cs-bentonite an excellent alternative for conventional sorbent materials.