In the fetal magnetocardiography project the magnetic activity of the fetal heart is measured. Fetal magnetocardiography (f-MCG) is a non-invase technique in which the magnetic field caused by electrical activity within the fetal heart is measured. As the magnetic fields over the maternal abdomen are tiny, superconducting devices are used to record these fields. Presently, these measurements are conducted in a magnetically shielded room, because fetal cardiac signals have only a very small magnitude. The very low magnetic fields are measured with liquid Helium cooled SQUID sensors. In the shielded room, the achieved white noise level is typically 10 fT/sqrt Hz while the peak magnetic field of the fetal heart is about about 3pT (= 3×10-12 T), when measured above the maternal abdomen.
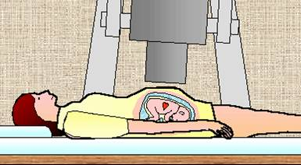
The existing fMCG measurement setup placed above the patient.
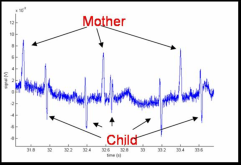
The graph shows the measured MCG signal (mother and child).
FHARMON
In the fetal hart monitor project (FHARMON) this technique is improved to be applied outside the shielded room in a standard clinical environment. The goal of this research is to demonstrate the functionality of an fMCG measurement system that contains two major improvements:
1 – A user friendly cooling system that is enclosed in a small box besides the patient, with a sensor head that can be positioned above the patient.
2 – A new noise reduction system that separates the fetal MCG signal form the environmental noise in a regular (=unshielded) environment
Artist impression of a future fMCG measurement setup
After completion of a working prototype the system will be placed in a hospital and became a usable option in the screening/diagnosis program for pregnancies. In this phase the research questions will shift from technology towards medicine, where the diagnostic abilities of this technology have to be demonstrated.
Recent results
We developed a SQUID based magnetic-detection system for fetal magneto-cardiography (fetal MCG) with a dedicated cooling system that can be operated without a magnetically shielded room. The SQUID sensors are located in a measuring head and cooled by circulating helium that, in turn, is cooled by a cryocooler placed at a distance of ~1.5m from the measuring head. The interference from the coolers requires them to be separated from the sensor head. The measuring head can be rotated to allow for a movement to the position above the patient where the best signal can be obtained.

First working prototype of fMCG measurement setup
Recently we obtained the first preliminary results after a successful cool down of the system down to an operating temperature of 4.5 Kelvin, for the SQUID and gradiometers. We measured the Magneto Cardio-Gram (MCG) of the adult heart in real time with a bandpass filter and 50Hz noise suppression in real time:

Real time Magneto Cardio-Gram (MCG) of an adult heart
Averaging this result ~150 times gives a very clear MCG of the subject with an amplitude of approximately 30pT, measured in a regular lab/office environment.
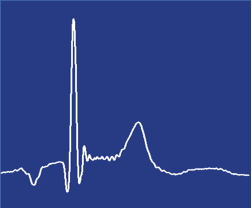
Averaged result for the Magneto Cardio-Gram (MCG) of an adult heart
