The assignment below is an example of an assignment that can be chosen within the research theme chemistry of battery materials. We can shape your assignment as a bachelor or a master assignment, and also include your own ideas and interests. Assignments on closely related topics, e.g. energy-efficient direct recycling of battery electrodes, or development of a sustainable Na cathode phase are also possible.
More information? Contact André ten Elshof
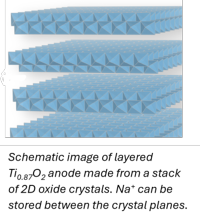
Assignment: Anode materials for Na ion batteries from 2-dimensional oxide building blocks
Titanium oxide-based phases have suitable redox potentials to serve as an anode in Na ion batteries and may be a safer alternative to the existing options. The anodes to be made in this assignment are so-called layered titanates, and they are prepared from a colloidal solution of 2D Ti1.73O4 building blocks.
The assignment will involve making such 2D crystal colloids using chemical synthesis methods, and to chemically transform these into solid NaxTi1.73O4 powders. The goal is to develop stable anode materials with a high concentration of sodium, fast Na ion migration through the material, and high cyclability of the electrodes (stability).
The energy density of the electrode (Wh/g), its power density (W/g) and its cyclability depend to a large extent on the details of the preparation process. These determine the final spacing between the layers, the organization of the layers relative to each other, and the stability of the stacked structure upon cycling Na+ in and out.
In this assignment titanate-based anode materials will be prepared, characterized and compared. You may choose your own strategy to prepare the best and most stable anode.
The assignment will involve chemical synthesis of 2-dimensional titanium oxide nanocrystals and its Na-anode derivatives, the use of x-ray diffraction (XRD) for phase analysis, electron microscopy (SEM) and the determination of the interlayer spacing, and X-ray fluorescence (XRF) to determine the atomic composition of the compounds. Selected electrodes will be tested electrochemically.
